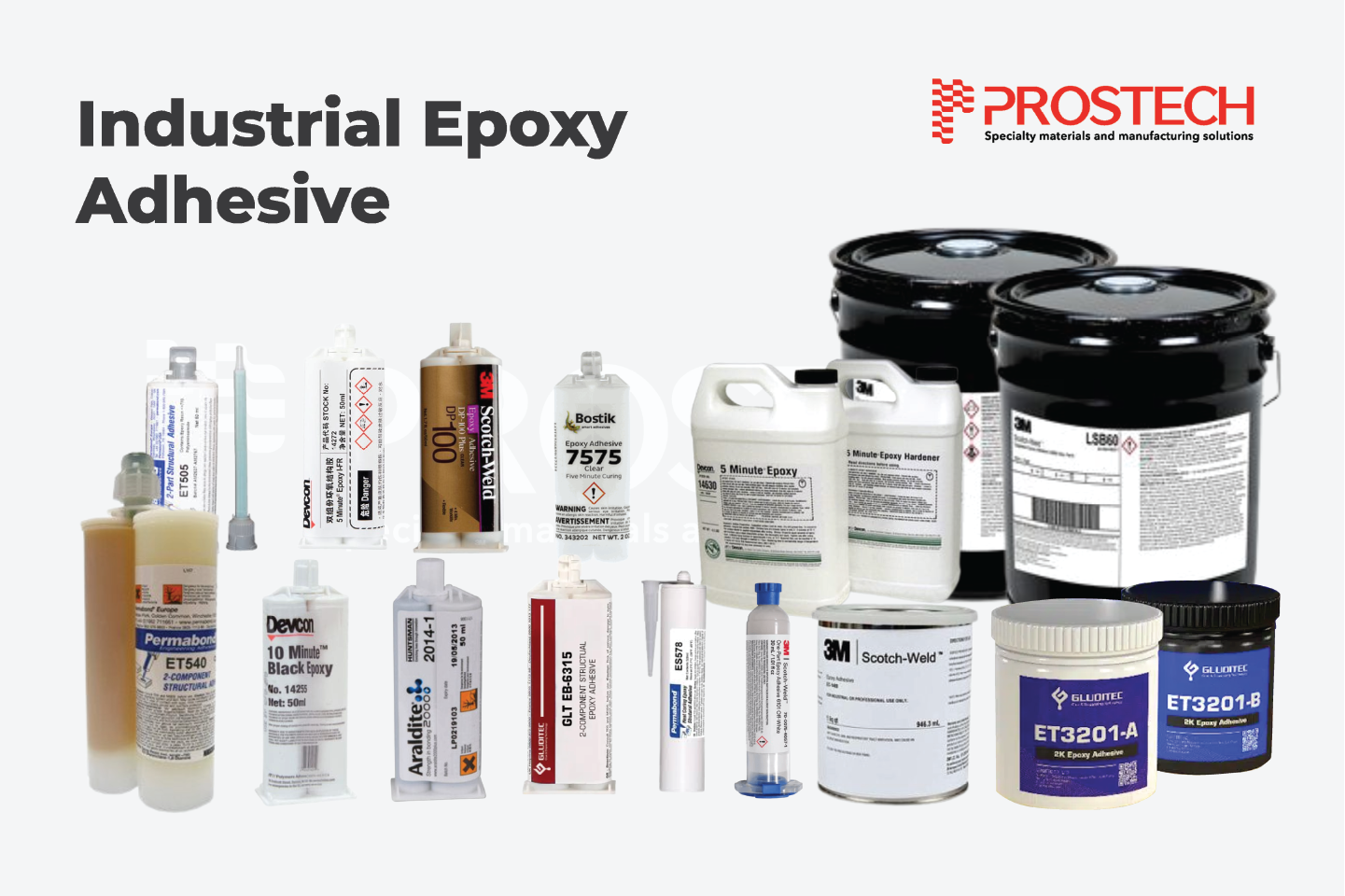
Although rubber is prized for its elasticity and flexibility, its chemical composition and surface properties often pose challenges when it comes to achieving strong adhesion. Bonding rubber can be more complex than bonding other materials due to its diverse forms and varied applications, each with specific electrical, thermal, chemical, or physical demands. To ensure a durable and reliable bond, selecting the right adhesive tailored to the rubber type and application is crucial.
When do we need to bond rubber?
Rubber bonding is essential in numerous applications across various industries. It is commonly required when rubber components need to be securely attached to other materials like metal, plastic, or even other rubber parts to create functional assemblies.
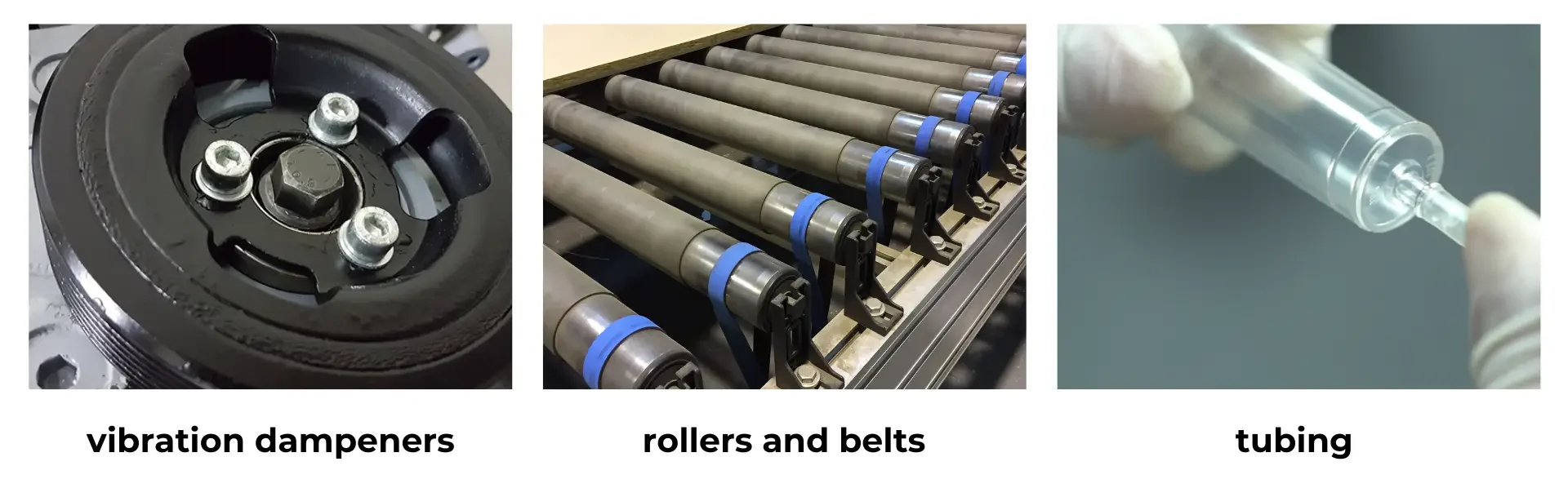
For instance, in the automotive sector, rubber bonding is critical for making seals, gaskets, and vibration dampeners. In industrial machinery, it ensures the durability of rollers and belts. Medical devices often rely on bonded rubber for flexible tubing or protective covers. Bonding rubber is also crucial in consumer goods, such as footwear and electronics, where durability and functionality are key. Whenever strength, flexibility, or environmental resistance is required in a product, bonding rubber becomes a vital step in the manufacturing process.
Why rubber type matters for bonding
Each type of rubber has distinct properties, such as flexibility, chemical resistance, and surface energy, which determine the compatibility with specific adhesives:
- Low surface energy: Some rubbers, like silicone and EPDM, require primers or specialized adhesives to achieve strong bonds.
- Plasticizer migration: Rubbers like NBR, SBR, EPDM,… may release plasticizers over time, affecting long-term bond performance.
- Environmental conditions: Certain rubbers excel in extreme temperatures or harsh environments, requiring adhesives designed for those conditions.
Surface Preparation for Rubber Bonding
Proper surface preparation is critical for achieving strong and durable rubber bonding. Rubber surfaces often carry contaminants like mold release agents, slip additives, or lubricants that can interfere with adhesion.
Cleaning the surface with a solvent such as isopropanol effectively removes these impurities, though aggressive solvents like acetone should be avoided as they may damage certain rubbers.
For improved adhesion, lightly roughening the surface through abrasion or using advanced treatments like plasma or chemical primers can significantly increase surface energy, particularly for low-surface-energy rubbers like silicone or EPDM.
Additionally, some rubbers contain plasticizers that can migrate to the surface over time, so using adhesives resistant to plasticizer migration is recommended. Ensuring the surface is clean, dry, and properly treated before applying adhesive is essential for a reliable and long-lasting bond.
Related article: How to bond Hard-to-bond Substrates (Nylon, COC/COP and PEBA) in Medical Devices Assembly?
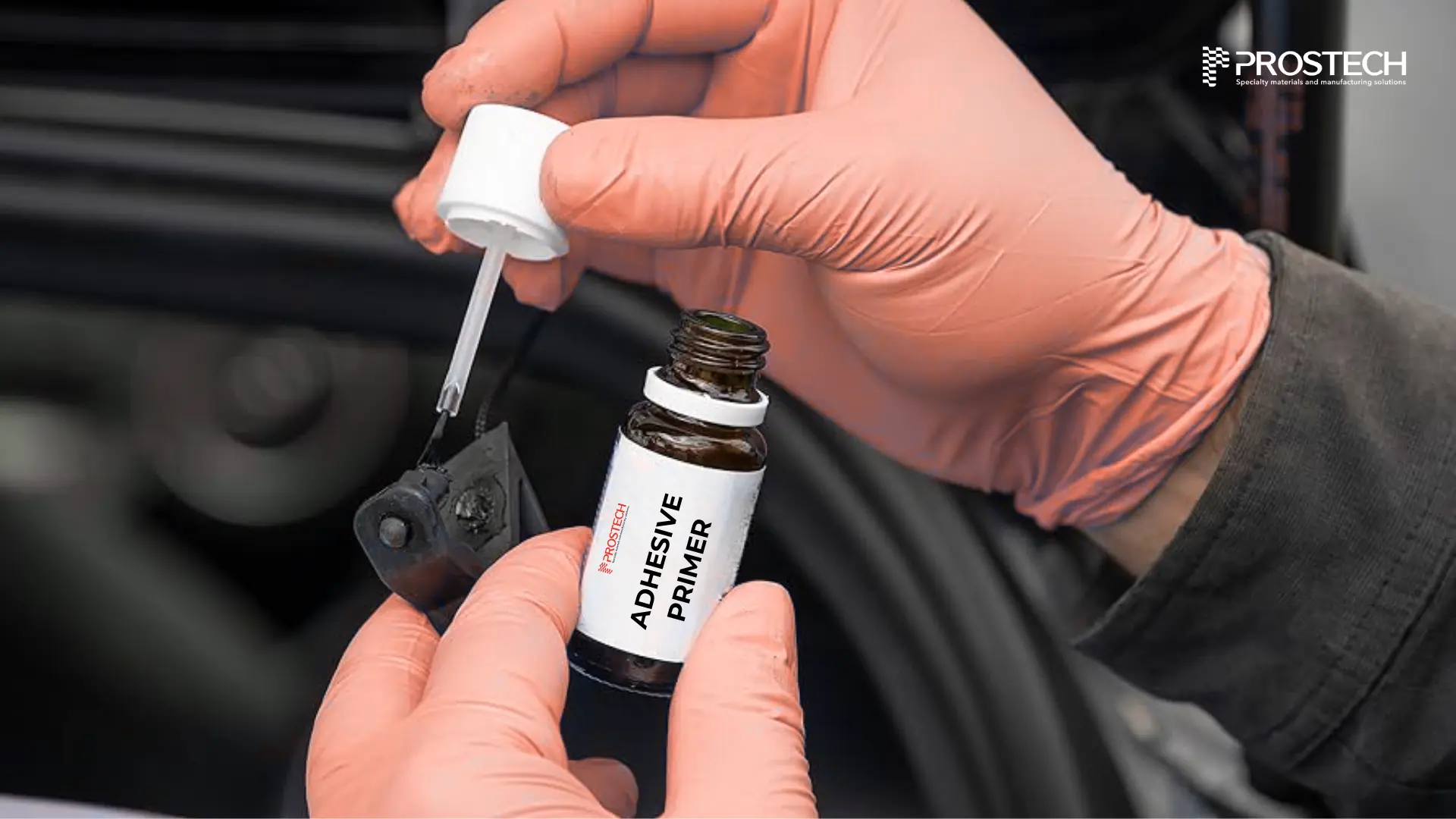

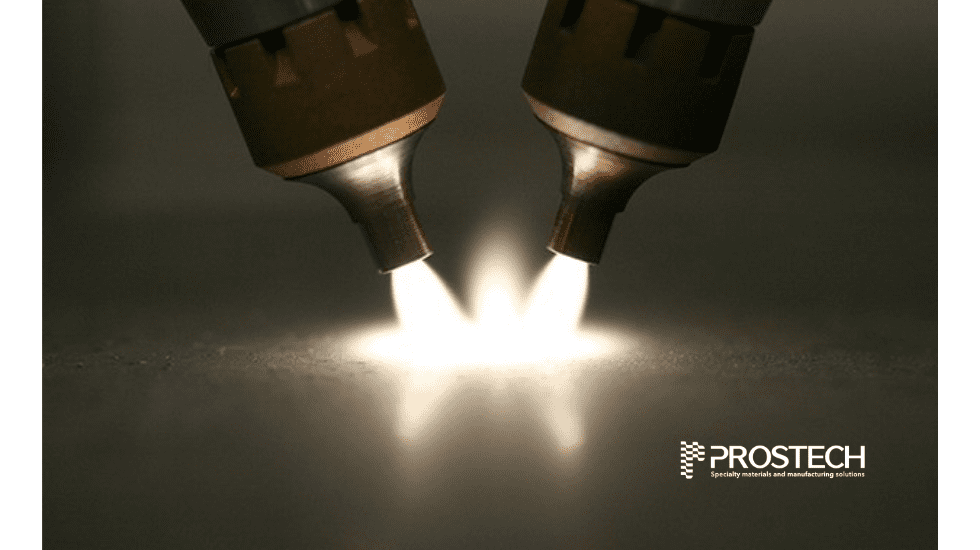
The best rubber adhesive for different rubbers
When choosing the best glue for bonding rubber, the type of rubber you are working with is a key factor to consider. Common types include nitrile rubber, butyl rubber, polyurethane rubber, silicone rubber, EPDM rubber, and natural rubber, which are widely used in products like hoses, gaskets, seals, and inner tubes. While cyanoacrylate adhesives, commonly known as super glue, are often the best choice for bonding most types of rubber, there are some exceptions and specific considerations for certain materials:
- Cyanoacrylate adhesives, more commonly known as super glue, are popular for their quick curing time, strong and reliable bonds, and suitability for small-volume applications. They work well with most rubbers, including natural rubber and NBR, when paired with a specialized hard-rubber adhesive that simplifies the bonding process by eliminating the need for a primer. There are certain cyanoacrylate adhesives specifically formulated to bond EPDM without requiring a primer.
However, cyanoacrylate adhesives are highly restrictive in terms of gap fill, with an effective range of less than 0.5mm, making them unsuitable for applications that require bridging larger gaps. Their rapid curing time, while beneficial for speed, allows little to no time for repositioning or adjustments after assembly. For silicone rubber, a primer is essential before applying cyanoacrylate adhesives to ensure strong adhesion. - Silicone adhesives are another excellent option for bonding silicone rubber due to their resistance to UV, temperature, chemicals, and moisture. They also provide flexibility and electrical insulation, making them ideal for specialized applications like soft O-rings.
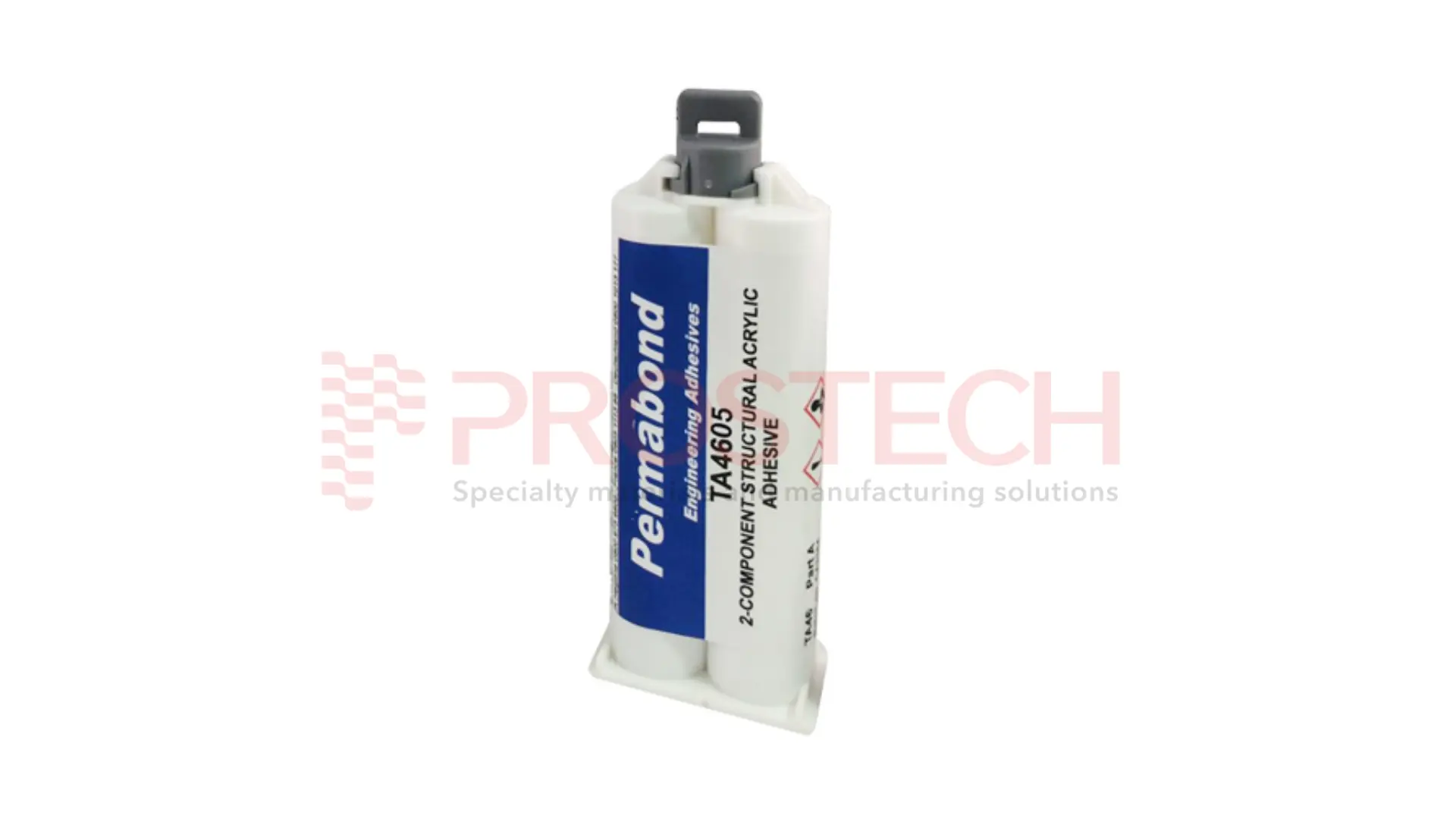
- Structural acrylic adhesives can be a great alternative for EPDM rubber, which contains polypropylene. These adhesives offer slower curing times, allowing for precise alignment and spreading during bonding. This makes them a practical choice for applications requiring accuracy and careful assembly.
Product recommendations:
| This adhesive is engineered for outstanding performance on challenging plastic and rubber substrates, such as heavily plasticized PVC, EPDM, ABS, Nylon, Santoprene, and Viton. Its fast-curing formula makes it ideal for high-efficiency applications. | |
|
|
Perfect for achieving a flexible bond with rubber, especially when used with primer. It provides reliable adhesion for rubber materials and is suited for specialized bonding needs. |
|
|
This one-component, oxime-curing silicone adhesive sealant cures at room temperature, forming a durable elastomeric rubber. It adheres seamlessly to various substrates like metals, plastics, ceramics, and glass without requiring a primer. |
|
|
A two-part acrylic adhesive specifically designed for bonding EPDM rubber and hard-to-bond plastics such as polypropylene, polyethylene, and PTFE. It offers excellent environmental durability, making it suitable for applications exposed to water and other challenging conditions. |
Bonding Rubber to Other Substrates
Bonding rubber to rubber can already be a complex process, but bonding rubber to other materials such as plastic, metal, or glass presents even greater challenges. The adhesive that works best for rubber-to-rubber bonding may not be suitable for connecting rubber to other substrates. Choosing the right adhesive requires understanding the properties of both materials involved and the desired outcome for the bond.
Cyanoacrylate adhesives are often the go-to choice for bonding rubber due to their quick curing time and strong adhesion. Acrylic adhesives are highly versatile and offer numerous options for bonding rubber to other surfaces such as metal, plastic, and more. For smaller or more intricate projects, fast-curing silicone compounds can also be an ideal solution. These compounds are not only versatile but also offer good flexibility and resistance to environmental factors, making them suitable for various substrates.
Ultimately, selecting the appropriate adhesive depends on the specific materials and the application requirements.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Rubber Bonding
Weak Bond: If the bond lacks strength, inspect for contaminants such as oils, mold release agents, or dirt on the surfaces. Also, check if the adhesive was applied in the correct quantity and if the curing process was completed under the recommended conditions.
Adhesive Failure: Ensure that the adhesive is compatible with the type of rubber being bonded. Using the wrong adhesive for the specific type of rubber can lead to poor adhesion or even complete failure. Some adhesives may not work effectively with specific rubbers, such as silicone or EPDM, without the use of primers or specialized adhesives.
Delamination: If the bonded surfaces separate over time, this could indicate insufficient surface preparation. Verify that the surface was cleaned, roughened, or primed as needed before adhesive application to create a proper bond.

Need More Help?
The choice of the appropriate adhesive for rubber bonding depends on the specific requirements of the application and environmental conditions. Each type of material offers its own advantages and is suited to different demands during the manufacturing and usage processes. With many years of experience in the industrial material, Prostech is ready to assist customers in selecting the right adhesive and providing integrated solutions for production lines to optimize manufacturing efficiency. Contact us for free consultation.