From securing threads in machinery to creating leak-proof seals in critical pipelines, anaerobic adhesives play a crucial role across various industries. But what exactly are anaerobic adhesives, and how do they work? In this article, we will explore the unique properties and working mechanisms of anaerobic adhesives to optimize performance and ensure reliability in even the most demanding environments.
Prostech’s anaerobic adhesive solutions
What is Anaerobic Adhesive?
Anaerobic adhesive is a specialized bonding material that cures (hardens) when deprived of oxygen and exposed to metal surfaces. Unlike conventional adhesives that need air or specific curing agents, anaerobic adhesives remain in liquid form when exposed to air but transform into a solid, durable bond in the absence of oxygen.
They are specifically designed for fastening and sealing applications that require a tight seal without relying on light, heat, or oxygen.
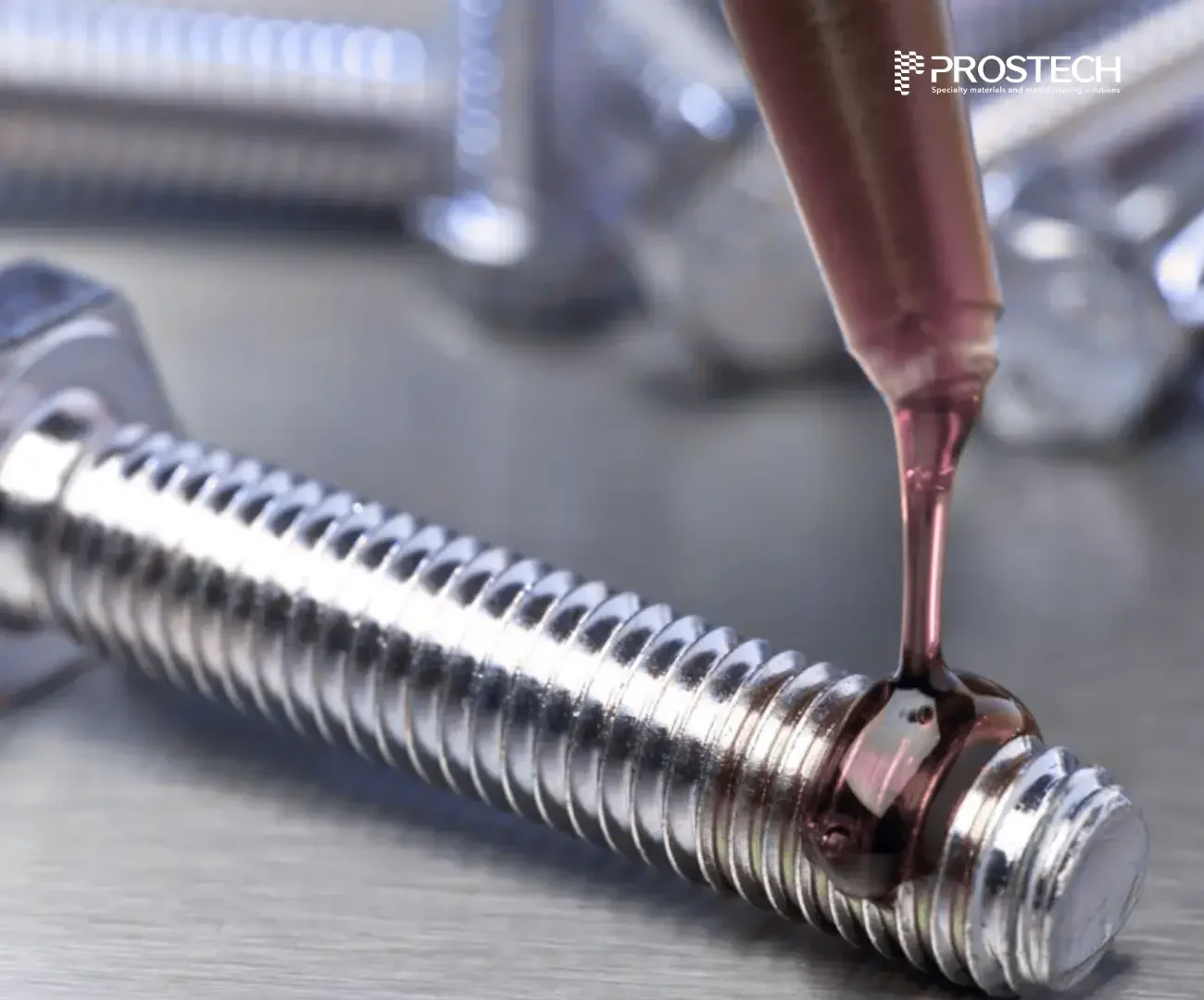

How Does Anaerobic Adhesive Work?
Anaerobic adhesives are distinct because of their specialized curing process. The composition generally includes a polymer with a polymerizable side chain, an organic acid (such as a vinyl or methacrylic group), a polymerization catalyst, and often a vinyl monomer. These adhesives remain stable and in liquid form when exposed to air and cure at room temperature through a free-radical mechanism:
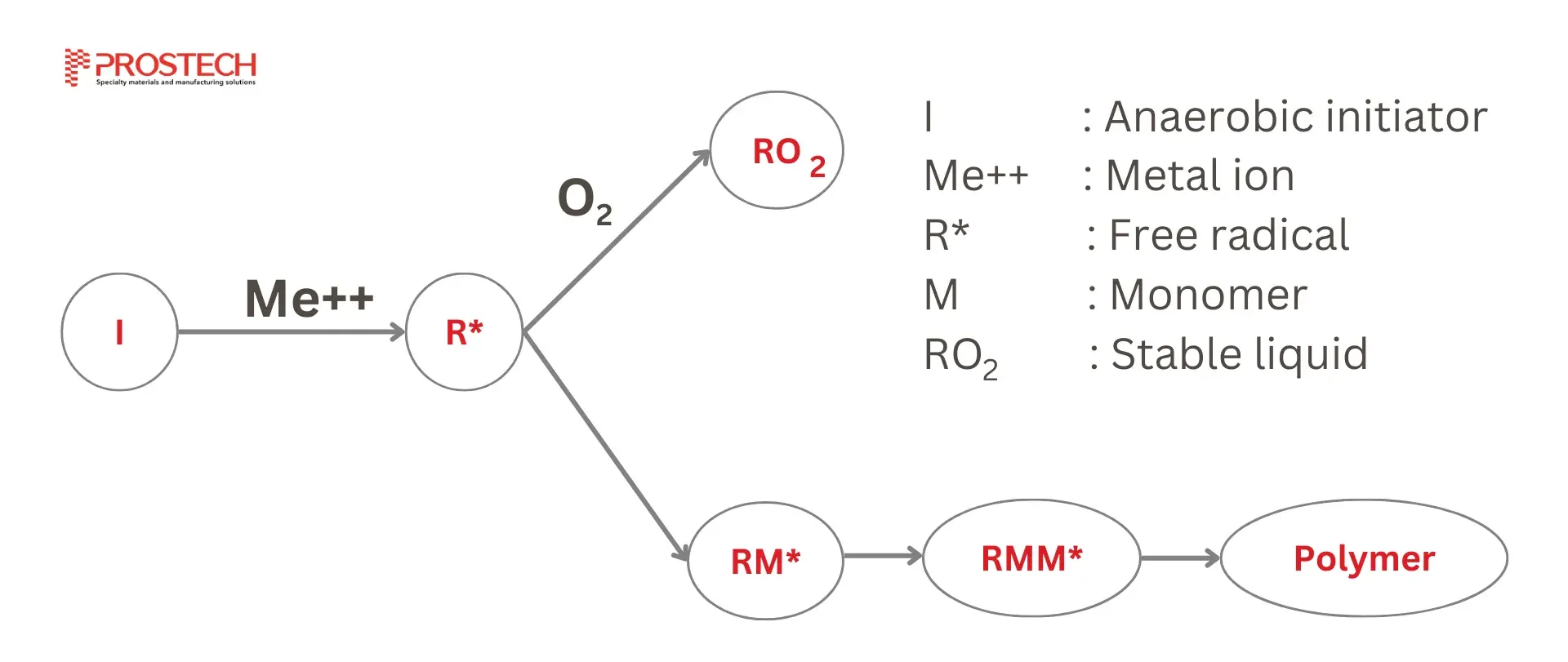
When the adhesive is applied to one side of a metal surface, it interacts with metal ions, causing the anaerobic initiators to decompose into free radicals. These free radicals are unstable but remain inactive in the presence of air, allowing the adhesive to stay liquid.
As the second substrate is joined to the first, oxygen is excluded from the adhesive layer. This absence of oxygen enables additional interactions between the anaerobic initiators and metal ions, producing more free radicals. These radicals react with nearby monomers, making them unstable and initiating a chain reaction of polymerization. Over time, the monomers react with each other, forming a solid, polymerized adhesive layer.
The curing process begins almost immediately and achieves full strength within about 24 hours, resulting in a durable bond capable of resisting vibrations, shocks, and extreme temperatures—perfect for challenging industrial applications. Adhesive that remains exposed to air, such as at the joint edges, may not cure but does not compromise the bond’s integrity within the joint. If necessary, an activator can be used to address any uncured areas.
Factors Influencing Curing Speed
The curing speed of anaerobic adhesives can vary depending on several factors, including:
1. Type of Metal Surface
The type of metal significantly affects how quickly anaerobic adhesives cure. Active metals like steel, copper, or brass accelerate the curing process due to their high reactivity. Passive metals like stainless steel, aluminum, or zinc may slow the reaction, often requiring primers to accelerate curing.
Reactivity Levels:
| Very Active | Active | Less Active | Passive |
|
|
|
|
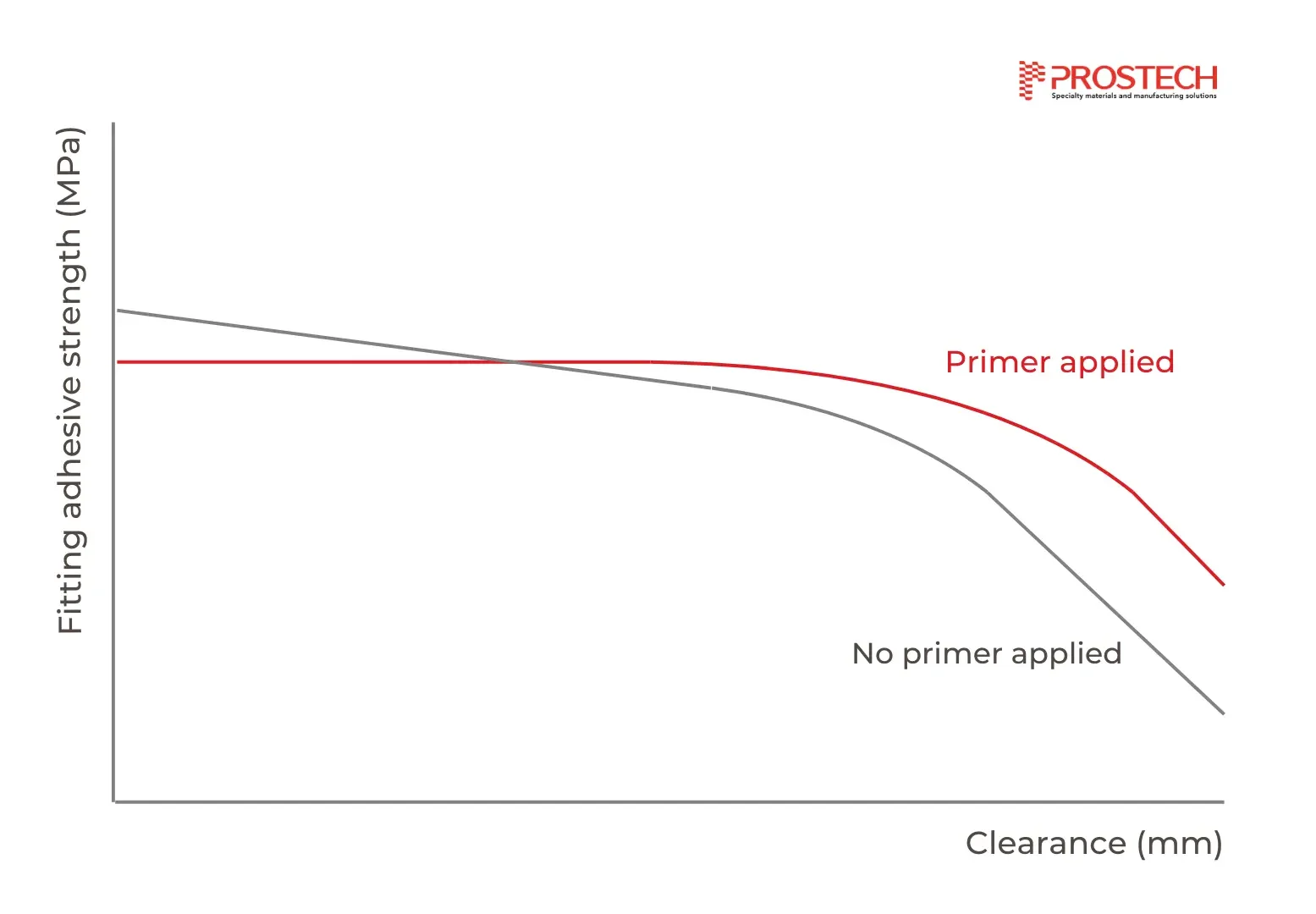
2. Surface Preparation
Surfaces must be clean, dry, and free of contaminants like oil, grease, or rust, as these can interfere with the curing process. Using primers is particularly helpful for passive or less reactive metals, as they enhance adhesion and ensure consistent curing under difficult conditions.
Prostech’s surface treatment solutions
3. Gap Size
Smaller gaps enable quicker curing by minimizing oxygen exposure and promoting closer contact between the adhesive and the metal surfaces. Larger gaps can slow down curing, as more adhesive is required to fill the space and polymerize. Adhesive viscosity and the maximum recommended gap size are typically provided in technical data sheets.
4. Temperature
Higher temperatures increase the reaction rate, leading to faster curing. Lower temperatures slow down the curing process, potentially requiring extended time or additional activators. Generally, increasing the temperature by 8–10 degrees Celsius approximately doubles the curing speed.
Key Applications of Anaerobic Adhesives
Anaerobic adhesives are essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing due to their ability to create high-strength, chemical-resistant bonds. These properties make them ideal for applications demanding durability and reliability. The adhesives are available in various strengths and viscosities, tailored for specific uses, including:
- Thread Locking: Secure bolts, nuts, and screws to prevent loosening caused by vibration or shock.
- Pipe Sealing: Seal threaded pipes and fittings to ensure leak-proof connections, commonly used in plumbing and gas systems.
- Retaining: Fix cylindrical components like bearings or shafts in housings to enhance load-bearing capacity.
- Gasketing: Replace traditional gaskets in flange assemblies, providing a strong, pressure-resistant seal capable of withstanding high temperatures.
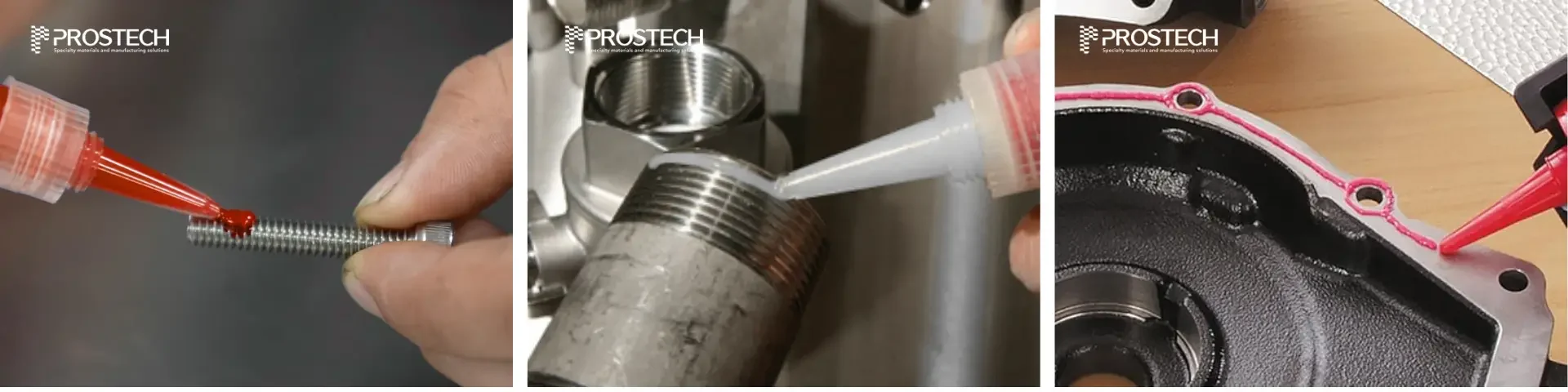

While anaerobic adhesives offer exceptional strength and rigidity, they are less suitable for structural applications requiring flexibility to withstand peeling forces. Additionally, viscosity plays a key role in determining the adhesive’s suitability for specific applications, ensuring it can fill gaps effectively or flow as needed for the intended use. For specific applications, you can reach out to us for personalized consultation:
Advantages of Anaerobic Adhesives
- High Strength: Provides a robust bond capable of withstanding heavy loads and mechanical stress.
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to oils, fuels, and other industrial fluids, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- High-Temperature Tolerance: Can withstand temperatures up to 200°C under continuous use, with certain advanced formulations enduring up to 230°C in constant exposure.
- Ease of Application: Simple to apply and requires no mixing or special curing conditions.
- Cost-Effective: Eliminates the need for additional sealing or locking hardware, reducing overall costs.
Limitations of Anaerobic Adhesives
While anaerobic adhesives offer numerous advantages, they also have some limitations:
- They are specifically designed for metal-to-metal bonding and may not perform well with non-metallic materials.
- Proper surface preparation, such as cleaning and degreasing, is essential to ensure optimal adhesion.
- They may require primers for certain metals like stainless steel or aluminum, which have low reactivity.
Prostech’s Anaerobic Portfolio
Prostech offers a comprehensive range of anaerobic adhesives tailored to meet the diverse needs of industrial applications. Our portfolio features excellent resistance to vibrations, good resistance to shear and fatigue stress, and prevents leakage and corrosion.
Product Recommendations:
|
|
A high-strength anaerobic adhesive designed for locking and sealing threaded fasteners to prevent loosening due to vibration. Ideal for applications requiring permanent assembly. |
|
|
3M offers a variety of anaerobic adhesives under the Scotch-Weld brand, providing solutions for threadlocking, pipe sealing, and gasketing applications. |
|
|
A single-component, solvent-free anaerobic adhesive designed for sealing and locking metal fittings and pipes, curing at room temperature to form a seal inert to hydrocarbons, most acids, solvents, and steam. |
See all Anaerobic Adhesives available
The choice of the appropriate anaerobic adhesive depends on the specific requirements of the application and environmental conditions. Each type of adhesive offers its own advantages and is suited to different demands during the manufacturing and usage processes. With many years of experience in the industrial material, Prostech is ready to assist customers in selecting the right adhesive and providing integrated solutions for production lines to optimize manufacturing efficiency. Contact us for free consultation.