Heat Transfer Fluids (HTFs), commonly referred to as coolants, play a critical role in the functional transfer of heat across a wide range of industrial, automotive, and commercial systems. These fluids are specifically engineered to absorb, transfer, and dissipate heat effectively, ensuring optimal thermal regulation and system efficiency. This blog explores what coolants are, the difference between ethylene glycol (EG) and propylene glycol (PG)-based fluids, and how to select the right coolant based on technical requirements.
What Is a Coolant?
A coolant is a specialized fluid used to absorb, transfer, and dissipate heat from equipment or machinery to prevent overheating and maintain optimal operating temperatures. A coolant circulates through systems such as engines, industrial equipment, HVAC units, or electronic cooling setups—carrying excess heat away from hot components and releasing it through a heat exchanger or radiator.
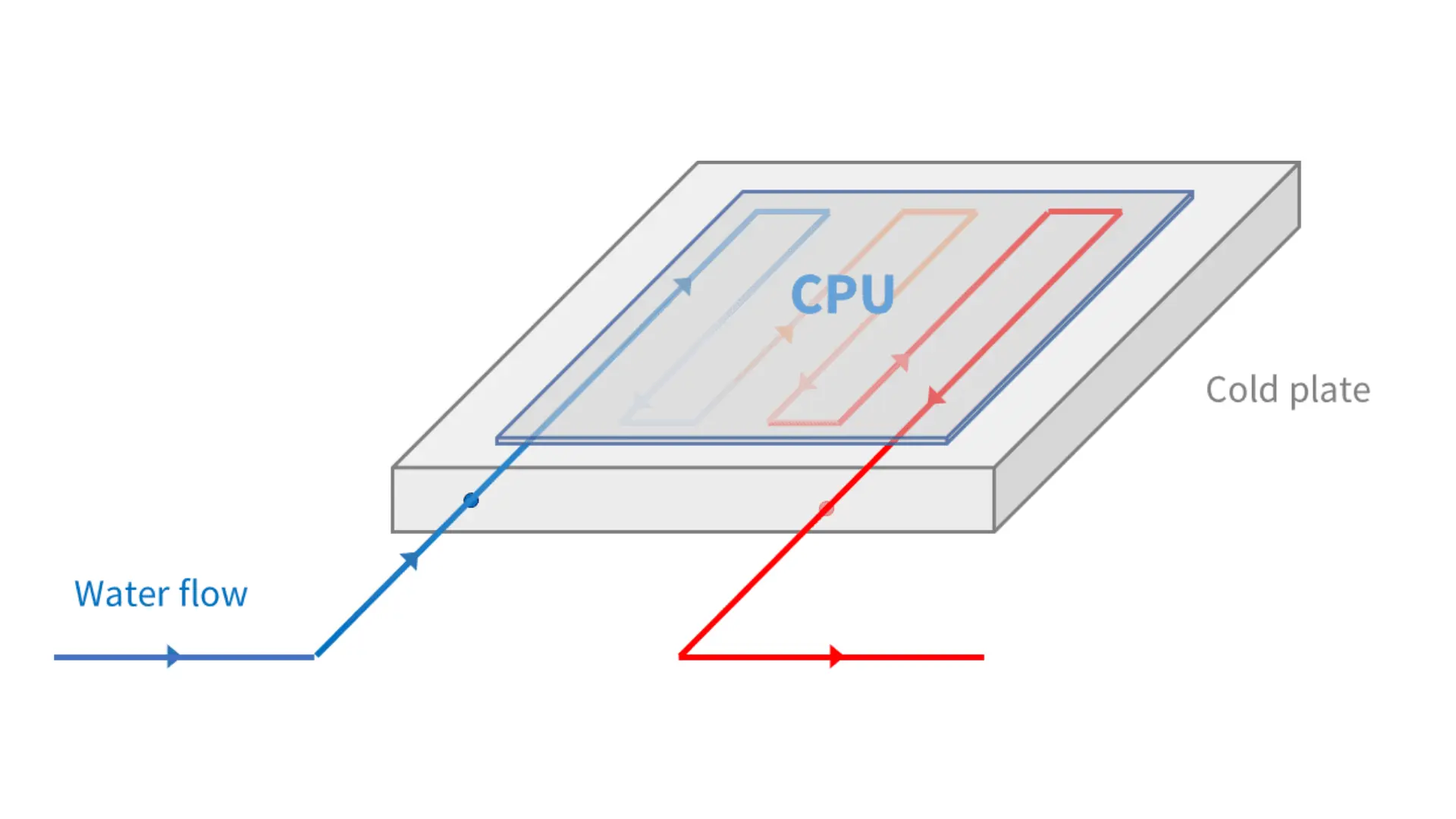
Heat transfer fluids are designed with specific thermal, chemical, and physical properties to ensure efficient heat transfer while protecting system materials from corrosion, freezing, boiling, or degradation over time. They may be water-based or glycol-based (e.g., ethylene glycol or propylene glycol), depending on the application and operating conditions.
Related article: Immersion Cooling vs Direct-to-Chip Cooling for Data Centers
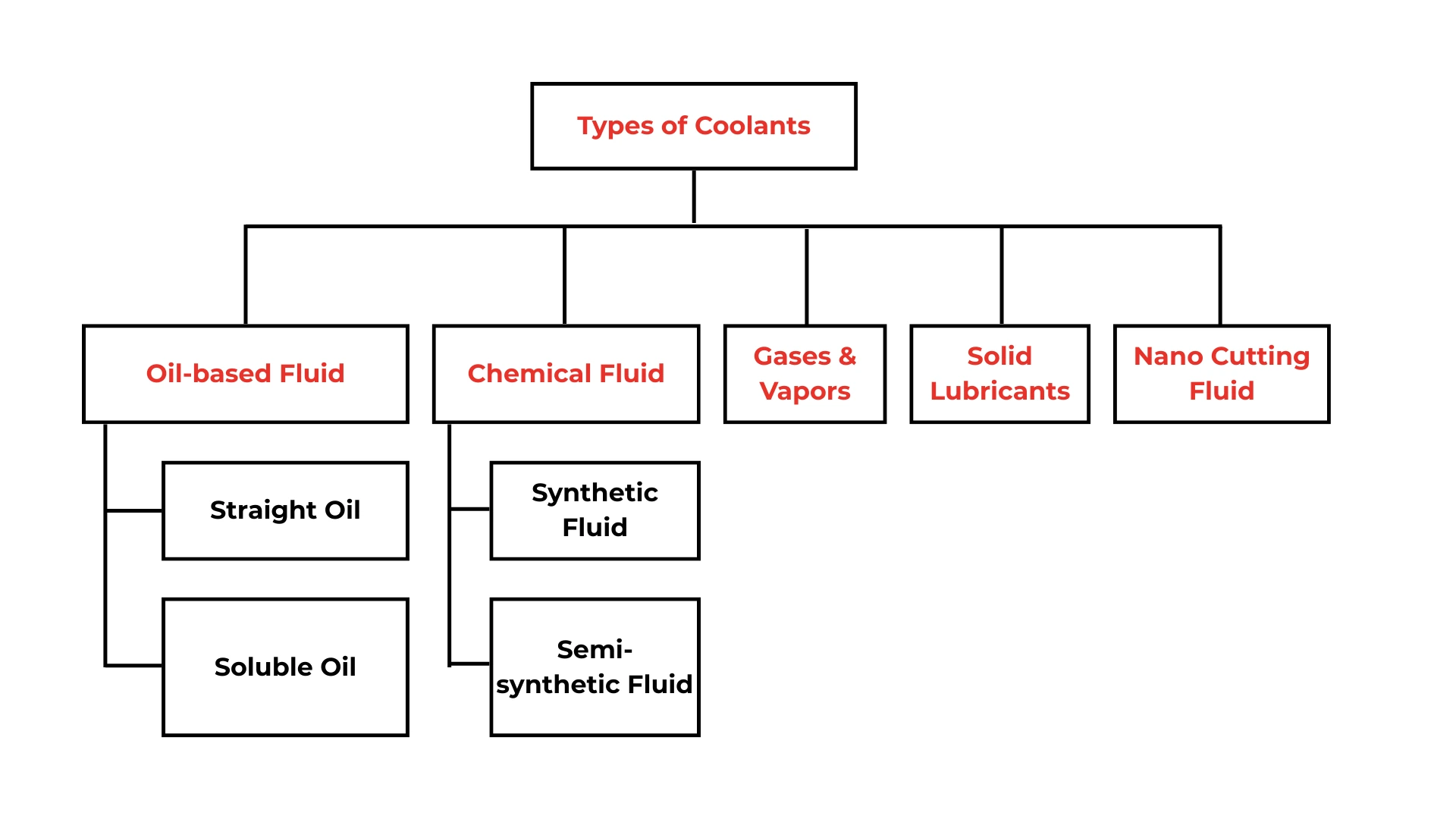
A broad classification of coolants used is shown following:
EG vs PG-Based Heat Transfer Fluids
Among the most widely used HTFs are Ethylene Glycol (EG) and Propylene Glycol (PG) based solutions.
While they serve the same purpose—transferring heat—they differ in several key aspects:
|
Criteria |
Ethylene Glycol (EG) |
Propylene Glycol (PG) |
|
Toxicity |
High – hazardous if ingested |
Low toxicity; FDA-approved for food and pharma use |
|
Thermal Efficiency |
Higher thermal conductivity; more efficient heat transfer |
High thermal conductivity |
|
Viscosity |
Lower viscosity; better flow at low temperatures |
Higher viscosity; may reduce flow rate in cold environments |
|
Cost |
Generally less expensive |
More costly due to refined processing and safety advantages |
|
Typical Applications |
Automotive antifreeze, industrial cooling |
Data centers, HVAC, food processing, cosmetics, pharmaceutical equipment |
Technical Fluid Requirements: Selecting the Right Coolant
Choosing the right coolant for your system goes beyond thermal efficiency. Here are some of the key technical requirements to ensure long-term reliability and performance:
1. Corrosion Protection: A quality HTF must include corrosion inhibitors to protect metal components like aluminum, copper, and steel from rust and degradation. Poor corrosion control can lead to system failures and costly downtime.
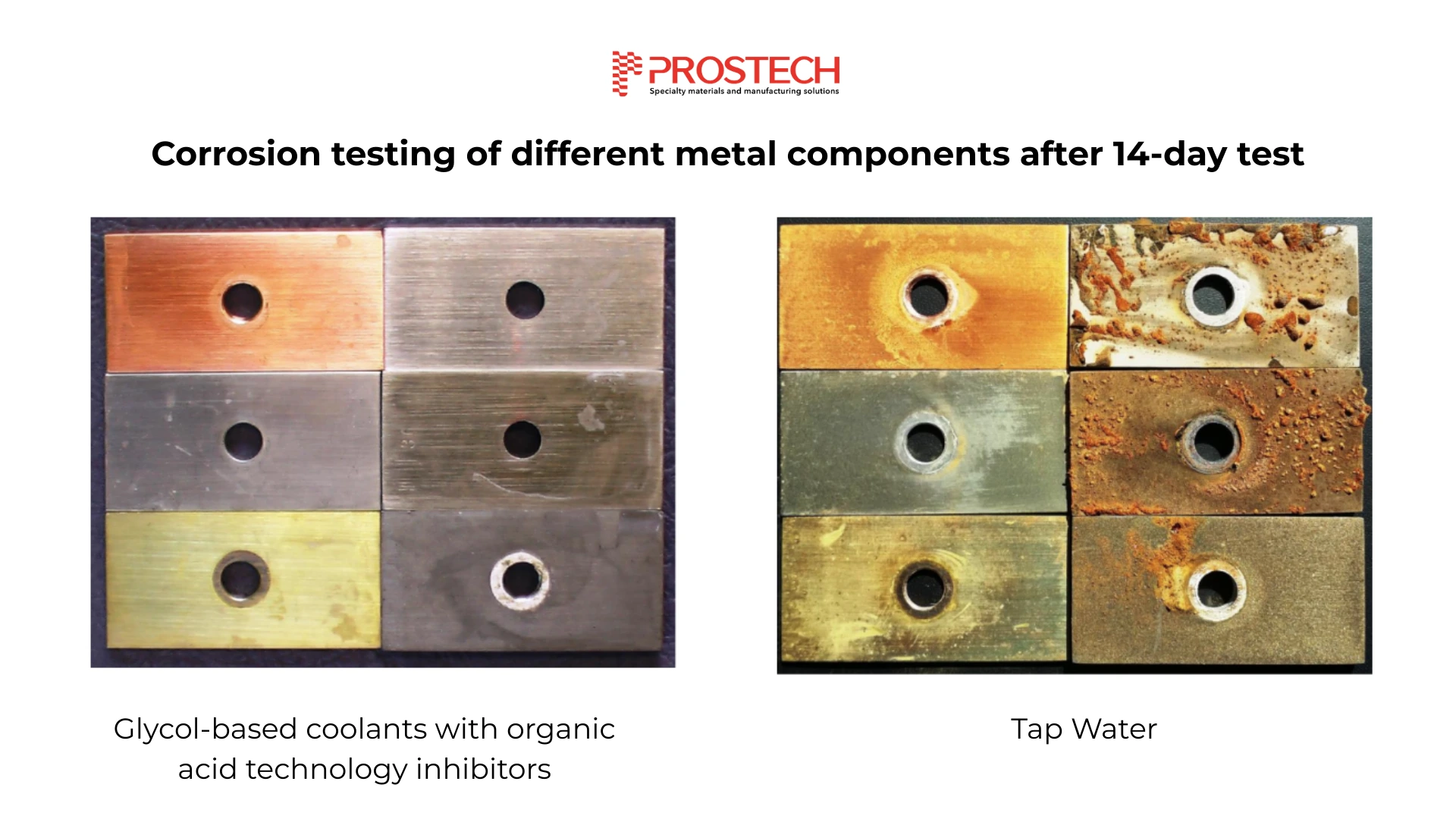
Glycol-based coolants like EG and PG, by themselves, are corrosive by nature. Organic Acid Technology (OAT) inhibitors—like those used in Recochem’s OAT PG-25—are designed to target only the active corrosion sites. They form a thin molecular film that inhibits corrosion without interfering with heat transfer, and they degrade very slowly, offering extended service life (up to 8 years).
2. Thermal Stability: The fluid must withstand high operating temperatures without breaking down or losing its properties over time.
3. Low Viscosity at Low Temperatures: Especially in low-temperature environments, fluid viscosity can directly impact pump efficiency and flow rate. A well-chosen coolant maintains optimal flow characteristics across the operating temperature range.
4. Compatibility: Coolants should be chemically compatible with system materials—seals, hoses, gaskets—to avoid leaks and material degradation.
5. Environmental & Regulatory Compliance: For industries like food processing or pharmaceuticals, coolants must comply with safety and environmental regulations such as FDA or USP standards (often requiring PG-based fluids).
Choosing the right Heat Transfer Fluid is critical to ensuring performance, safety, and cost-efficiency in industrial cooling. Whether you opt for EG or PG-based fluids, a well-selected HTF will protect your equipment, optimize energy use, and maintain smooth operations in the harshest conditions.
If you need expert advice on which fluid suits your application, contact our team today for technical consultation and customized solutions.