Up to 55% of failures on electronic circuit boards are caused by heat

Most electronics such as power transistors, CPUs and power diodes produce a significant amount of heat which may be necessary to take into account in order to prolong these electronics’ working life and increase reliability as well.
During the operation, the electronic component’s temperature will rise until the heat produced inside the device becomes equal to the heat lost to the surroundings and the device has reached its equilibrium. This temperature may be high enough to significantly shorten the shelf life of the component or even cause the device to fail.
The result in temperature increasing will affect the operation of the active and passive devices in the integrated circuits. If the temperature increase is high enough, the active or passive devices being heated may either not work properly or even totally fail. Such failures include thermal runaway, junction failure, metallization failure, corrosion, resistor drift, and electromigration diffusion. Therefore, it is crucial to minimize any temperature increase in an electronic package.
What causes temperature increase in an electronic package?
- Increasing power density and current levels
The insatiable demand for higher performance processors has led to a steady escalation in power consumption across all the market segments, such as mobile and performance desktops as well as servers and workstations. Increasing power density and current levels in the microprocessors have been main heat sources and cause concerns to do the thermal management of the on-chip hot spots as well as the package and interconnection Joule heating.
- Higher density of components in PCBs surface
Another cause for concern about thermal management on an electronic circuit board is, The electronic industry field is witnessing the increasing trend of thinner and smaller handheld devices and household appliances. That is why the PCB is more compact, the spaces among components on electronics PCBs are getting closer and closer, making the heat harder to transfer out of PCBs components.
So what should we do if the system of fan is not enough?

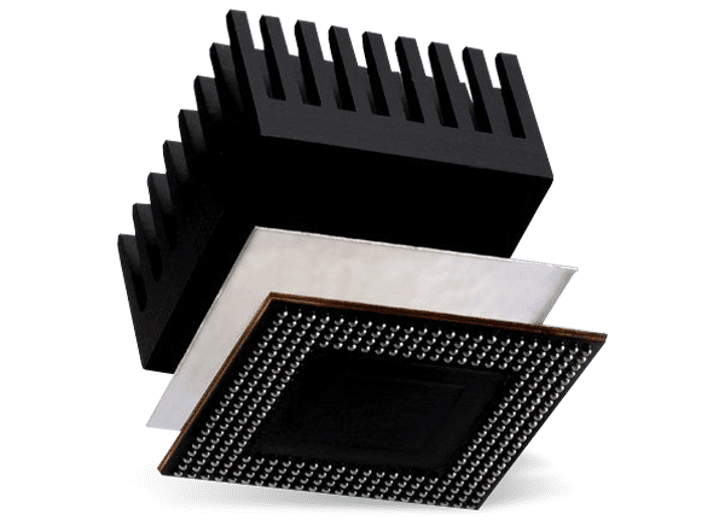
One way of limiting the operating temperature is increasing artificially the surface area. This is done by attaching a metal heat sink to the device. The choice of the heatsink is very important, cause the results depends on many factors including heatsink materials, size, conductivity, design and the adhesive to bonding it to the PCB as well.
Air is a poor conductor of heat and so the interface will provide a thermal barrier that limits the efficiency of heat loss from the device. It is to overcome this effect that thermal conductive compounds are used.
Thermal conductive compounds are designed to fill the gap between the device and the heat sink and thus reduce the thermal resistance at the boundary between the two. This leads to faster heat loss to the heat sink and lower operating temperature for the device. In electronics, these thermal conductive compounds are called thermal interface materials-TIMs.
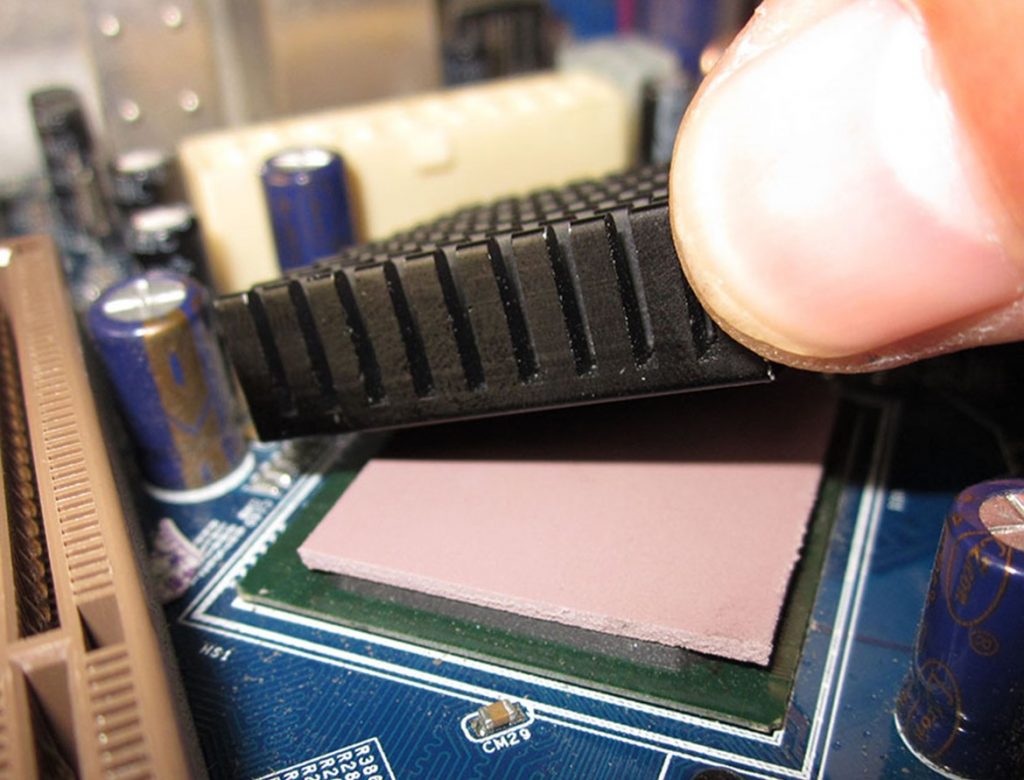
Learn more about how TIMs help to manage the produced heat on the PCB?
In conclusion, the choice of appropriate heatsink and thermally conductive materials is somehow difficult. As a result, Pros Technology is here to help our customer solve the problems, if have any questions or requirement for thermal management, please do not hesitate to contact us through below information: