
Based on the form of soldering materials, they can be categorized into the following main types that are widely used:
1. Soldering Material: Solder Wire
Learn more about solder wire in the article: What is Solder Wire? A guide to solder wire selection
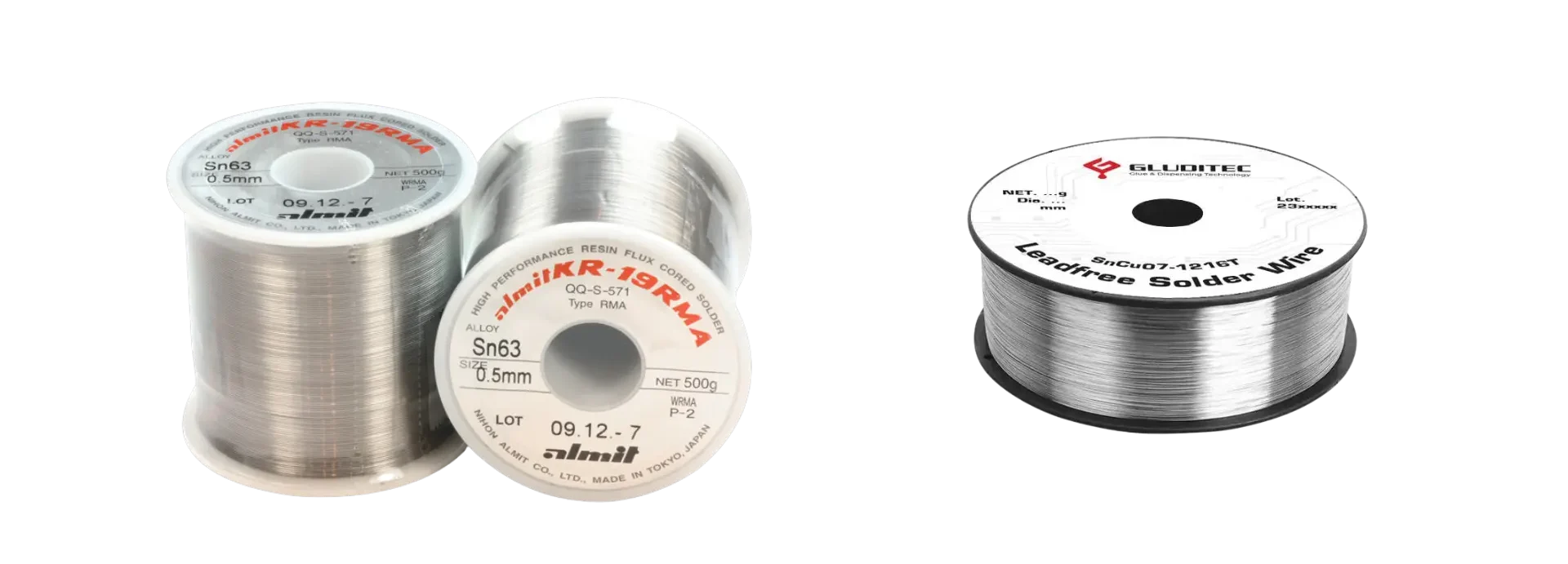

Leaded Solder Wire
Leaded solder wire is typically made from a tin (Sn) alloy with a ratio of lead (Pb) to create various soldering properties. Lead is a component with a low melting point, making it easy to use.
The product code usually indicates the composition that makes up that solder wire:
Sn63 Solder Wire (Sn-37.0Pb): 63% tin and 37% lead
Cuộn dây hàn Sn62 (Sn-2.0Ag-36.0Pb): 62% thiếc, 2% bạc và 36% chì
Cuộn dây hàn Sn8 (Sn-92Pb): 8% thiếc và 92% chì
Sn43 Solder Wire (Sn-43Pb-14Bi): 43% tin, 43% lead, and 14% bismuth
Lead-free solder wire
Lead-free solder wire is a type of soldering wire that does not contain lead, making it safer for both the environment and human health. This type of solder wire generally comes at a higher cost and is used in electronic devices imported into strict international markets such as Europe and the Americas. In lead-free solder products, tin (Sn) is often alloyed with silver (Ag) or copper (Cu) to maintain high electrical conductivity and durability.
Similar to leaded solder wire, the product code for lead-free solder wire also indicates the composition that makes up the solder wire. Some representative codes include:
Lead-free solder wire SAC305: Sn – 3% Ag – 0.5% Cu
Lead-free solder wire Sn-0.7Cu 228°C
Lead-free solder wire Sn-0.7Cu-2.0Bi-0.035Fe
Flux-Cored Solder Wire
Flux core solder wire is a type of electronic soldering wire that has a core containing flux with various chemical bases. The rosin core (flux) is designed to help the solder joint adhere more securely, remove residual contaminants from the surface after soldering, and produce high-quality solder joints.
Some representative codes include:
GUMMIX-21 Zeta LFM 23-S contains flux core L1
GUMMIX-19 CH LFM-48 (3.50%) contains flux core M1 (SAC305)
Halogen Free Leaded Solder Wire
Gummix HF LFM 48 contains flux core L0
GUMMIX-19 NH LFM-48 (3.50%) contains flux core L0
In addition to the alloy composition of solder wire, selecting the appropriate material depends on several other factors, such as melting temperature, type of flux, wire diameter, and soldering method. Each type of solder wire offers distinct advantages and meets different requirements. With many years of experience in industrial materials, Prostech is ready to assist customers in choosing the right soldering material and providing integrated solutions for production lines. Contact us for a free consultation!
Choosing the Right Solder Wire
2. Soldering Material: Solder Bar
Solder Bar is a type of soldering material in bar form, used in the Wave Soldering Assembly process. In this process, the solder bar is melted into a liquid state and then used in subsequent stages to assemble electronic components onto the circuit board.

Solder bars are typically made from a tin (Sn) and lead (Pb) alloy with varying ratios, the most common being 60/40 (60% tin and 40% lead). However, due to the trend of eliminating lead from manufacturing processes to protect the environment and human health, lead-free solder bars are becoming increasingly popular.

One of the most common solder bar products available today is the SAC305 solder bar/wire with a solid core – lead-free (Pb-free) with an ideal alloy ratio: 3% Ag, 0.5% Cu, and the remainder is tin (Sn). You can also explore other solder bar options such as:
| Product codes | Alloy Composition | Key Properties | Melting Temperature (°C) | Specific Gravity |
| PF606 | Sn/3.0Ag/0.5Cu/X | High purity | 217~219 | 7.4 |
| PF610 | Sn/3.0Ag/0.5Cu/0.06Ni/0.01Ge | Part of the commonly used SAC305 solder bar series | 217~219 | 7.4 |
| PF634 | Sn/1.0Ag/0.5Cu/0.04Ni/0.01Ge | Low Ag content | 217~226 | 7.4 |
| PF645 | Sn/0.3Ag/0.7Cu/0.04Ni/0.01Ge | Low Ag content, high purity | 217~226 | 7.3 |
| PF604 | Sn/0.7Cu | High purity | 227~228 | 7.3 |
Contact us for a free consultation on solder bars
3. Soldering Material: Solder Paste
Solder Paste is a bonding compound that consists of small solder alloy particles (typically lead-free) mixed with flux.
Solder paste is widely used in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) processes, where thousands of small components need to be soldered onto a PCB surface quickly. Solder paste is commonly used with automatic solder paste dispensing robots. This technology is applied in consumer electronics, telecommunications equipment, automotive, and many other industries.

Some commonly used types of solder paste today include:
Lead-Based Solder Paste
Formosa SH-6209RMA: 62% Sn – 36% Pb – 2% Ag
Almit SRC Sn62.8 (Sn – 0.4Ag-36.8Pb)
Almit SRC SJ-3Bi (Sn-38.0Pb-3.0Bi-1.5Ag-0.5Sb)
Lead-Free Solder Paste
Formosa PF606-P26: Sn/Ag3.0/Cu0.5/X
Solder Paste for Automated Dispensing Systems
LFM-48U MDA-5 (10-28µm) for jetting systems
LFM-89 NH-MDL for adhesive dispensing with laser
Sn62 SRC HM1 RMA (9.5%)
Low-Temperature Solder Paste
Low-temperature solder paste PQ10 138℃
Low-temperature solder paste PF735 138℃ – withstands high-temperature cycles
Solder paste needs to be stored at low temperatures to prevent oxidation and maintain the necessary viscosity for application. When using solder paste, operators must ensure that the amount applied to the PCB is adequate and correctly positioned, avoiding shortages or excesses that could lead to soldering defects. Additionally, the soldering process should be conducted in a clean environment free from dust to ensure high-quality solder joints.
Contact us for a free consultation on solder paste
4. Soldering Material: BGA Sphere (Solder Ball)
BGA Solder Balls are small spherical pellets made from a metal alloy, typically tin (Sn) combined with other elements such as silver (Ag), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), or bismuth (Bi). These solder balls are commonly used in applications where chips are directly mounted onto printed circuit boards (PCBs) using the Ball Grid Array (BGA) method, including PBGA, CBGA, TBGA, CSP, and Flip Chip.
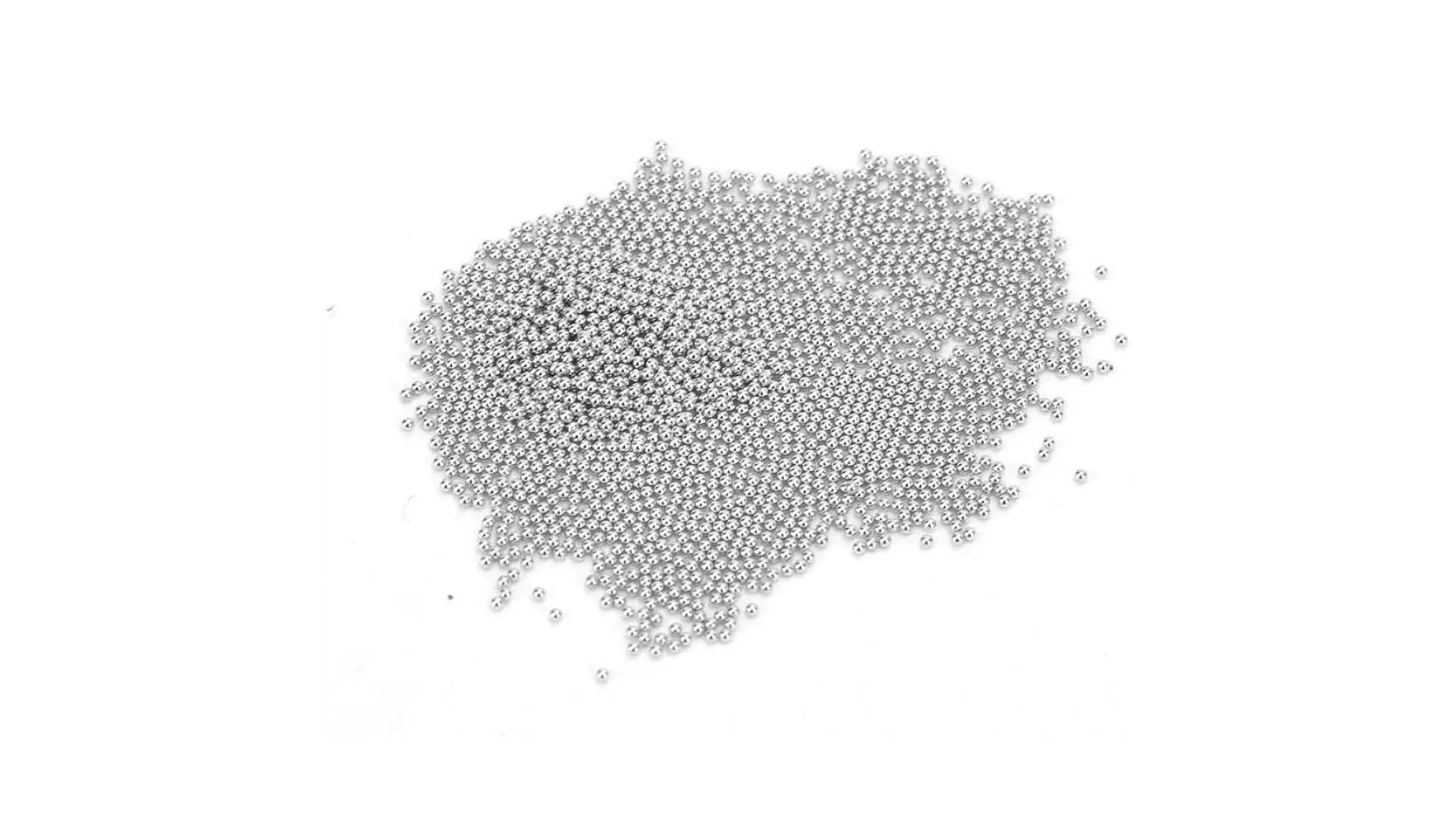
Some solder ball products include:
| Product Code | Diameter | Error number |
| BS76-50 | 0.76mm~0.50mm | ±20um |
| BS45-10 | 0.45mm~0.10mm | ±10um |
Using electronic solder balls requires precise temperature and heating time control to ensure the solder balls melt and form connections correctly. If the temperature is insufficient or uneven, it can lead to soldering defects such as incomplete melting of the solder balls or weak connections, resulting in functional errors in the device. Additionally, it is important to store solder balls in a dry environment and avoid exposure to moist air to prevent oxidation, thereby maintaining the quality of the solder balls.
Contact us for more detailed information
5. Flux
Flux is a material used to enhance the adhesion of solder materials (solder paste, solder wire, solder bar) to the surface of electronic circuits. The diverse applications and requirements in electronic assembly and semiconductor packaging drive the development of flux technology, resulting in various types of flux suited to different applications, such as:
No-clean Flux (NC)
It is a type of flux that leaves no residual residue on the soldered surface—suitable for high-volume production lines with less complex circuit surfaces, helping to reduce costs associated with cleaning flux residues.
- BM-1 RMA Flux – used for BGA, Flip Chip, and electronic circuit repair
-
BM-5000 RMA Flux – used for BGA and electronic circuit repair
Halogen-free Flux
It is a type of flux that does not contain halogens—volatile chemicals in the air that are not environmentally friendly and can cause rusting on circuit boards.
- SM-813 Flux – low viscosity, halogen-free
- SM-827 Flux – moderate viscosity, halogen-free
Water Soluble Flux
It is a type of flux that is safe and environmentally friendly, used in electronic applications due to its ease of cleaning after the soldering process.
Wave Soldering Flux
Used for high-volume production processes, this flux is designed for automatic dispensing onto circuit boards and offers excellent rust resistance.

When using flux, it is important to choose the type that matches the technical requirements of the product and the soldering process. Using the wrong flux can lead to issues such as poor solder joints, corrosion, or long-term reliability problems. Additionally, safety guidelines should be followed when working with flux, especially those with high corrosiveness.
Contact us for a free consultation on flux
6. Flux Remover
It is a type of chemical used to clean residual flux residues left on the surface of circuit boards after the electronic assembly process or for circuit repair. Typically, these residues from flux are difficult to remove and require a specialized cleaning chemical that does not affect the functionality of the electronic components on the circuit.

Environmentally safe flux cleaning agent – low VOC
Flux cleaning agent that is non-corrosive to plastics
Flux cleaning agent with UL94 flame retardant certification
Flux cleaning agent for lead-free solder materials
Solder material supplier
You can find solder materials at various building supply stores and supermarkets nationwide. Additionally, you can order from authorized distributors in Vietnam, such as Prostech, for the best prices.
Prostech is an authorized distributor of major brands such as Almit, Gluditec, Chemtronics, Shenmao,… With years of experience, Prostech has supplied products to thousands of manufacturers across the country. We have a nationwide storage network and provide logistics support to our customers. As a comprehensive supplier, Prostech continuously strives to be a trusted partner for manufacturers in Vietnam as well as on the international market. Contact us by leaving your information below:







