In the modern world, electronic devices are becoming more and more popular and complex, which makes the need to shield other devices as well as people from electromagnetic waves an important issue. Electromagnetic waves can adversely affect the performance of electronic devices and pose a risk to human health. From household appliances, mobile phones to industrial and military systems, electromagnetic interference can cause serious consequences such as disruption of operations, reduced performance and even complete failure. However, reducing the use of electronic devices is not always possible. Instead, we can focus on minimizing the intrusion of electromagnetic waves generated by these devices. This article will explain in detail the mechanism of electromagnetic interference protection and optimal solutions to ensure the safety and performance of devices.
Devices requiring EMI Shielding
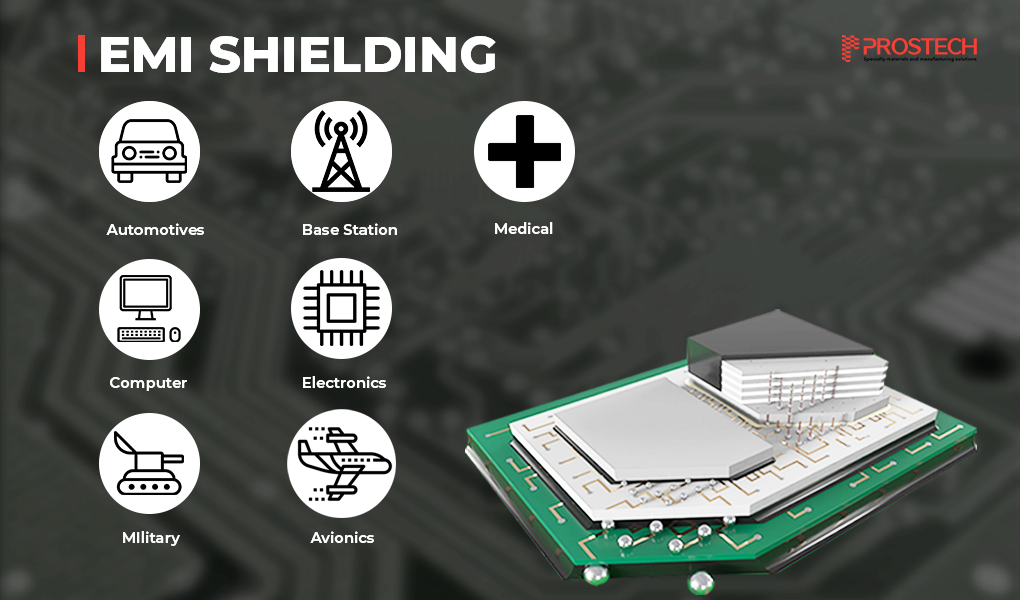

As technology advances, many electronic devices need to be protected from electromagnetic interference to ensure stable and efficient operation. Devices such as heart monitors, mobile phones, industrial control systems, and aerospace equipment, etc. are all at risk of electromagnetic interference, which can cause disruptions and reduced performance. To ensure stable and accurate operation, electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection for these devices is essential. Here are some typical devices and components that require EMI protection measures:
Development of EMI Shielding technology for electronic devices
Today’s electronic devices are constantly improving in both technology and design, forcing manufacturers to continuously upgrade their manufacturing technology. One clear trend is the miniaturization and tight packaging of sensitive components. The explosion of wireless technologies has also increased the need for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding for electronic components and devices. In this context, EMI shielding methods have made significant advances:
EMI Shielding at the circuit board level
This method uses conductive materials soldered onto the circuit board, which is one of the more traditional methods. However, this method requires a large amount of space and increases the weight and thickness of the design, making it more difficult to repair. Despite these limitations, board-level shielding is still an effective solution for many applications that require strong protection.
EMI Shielding at the component level
This method uses conductive materials integrated directly onto the component itself, allowing for higher component density on the circuit board, creating more flexible designs, helping to produce smaller, thinner, and lighter devices.
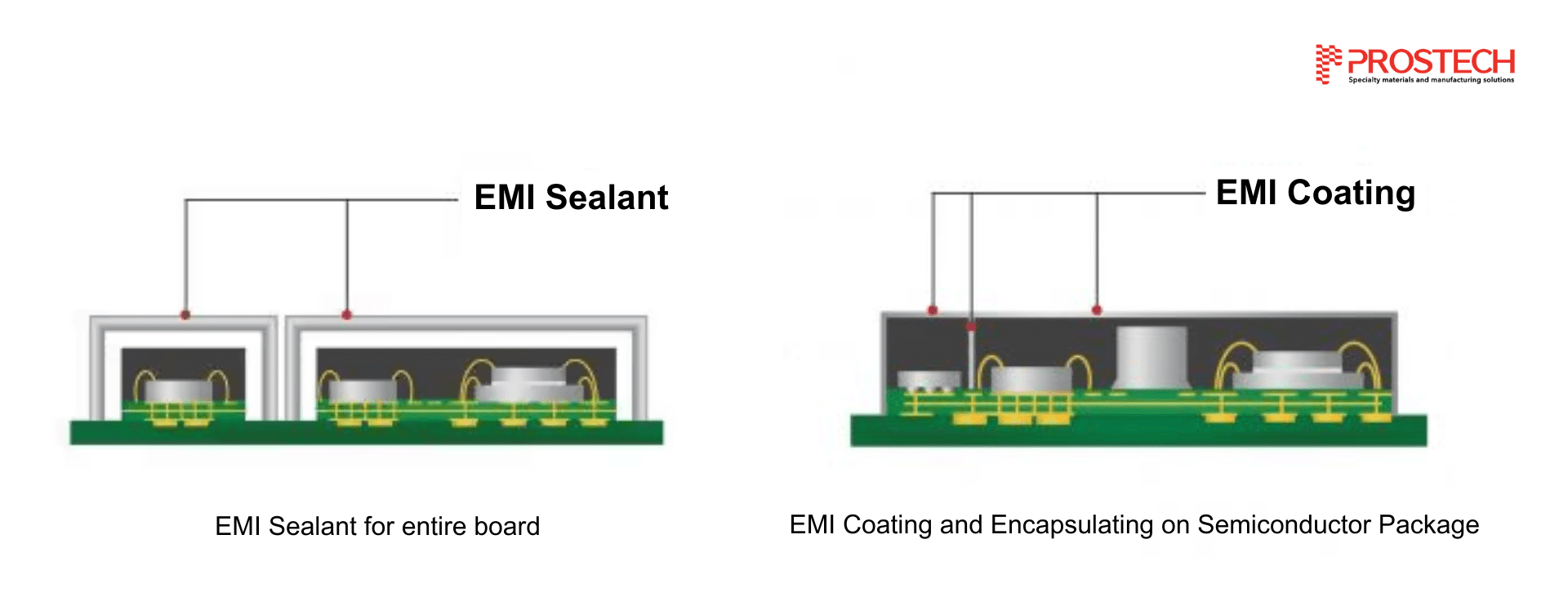

Mechanism of EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding is the use of a shield (a shaped conductive material) to enclose part or all of an electronic circuit. This circuit may be a source or a receiver of electromagnetic interference. Thus, it limits the amount of electromagnetic wave energy emitted from the surrounding environment that can penetrate the circuit board and, conversely, affects the EMI energy generated by the electronic circuit that can escape into the external environment.
Shielding can absorb or reflect electromagnetic waves through conductive or magnetic materials. There are three main mechanisms in electromagnetic interference protection:
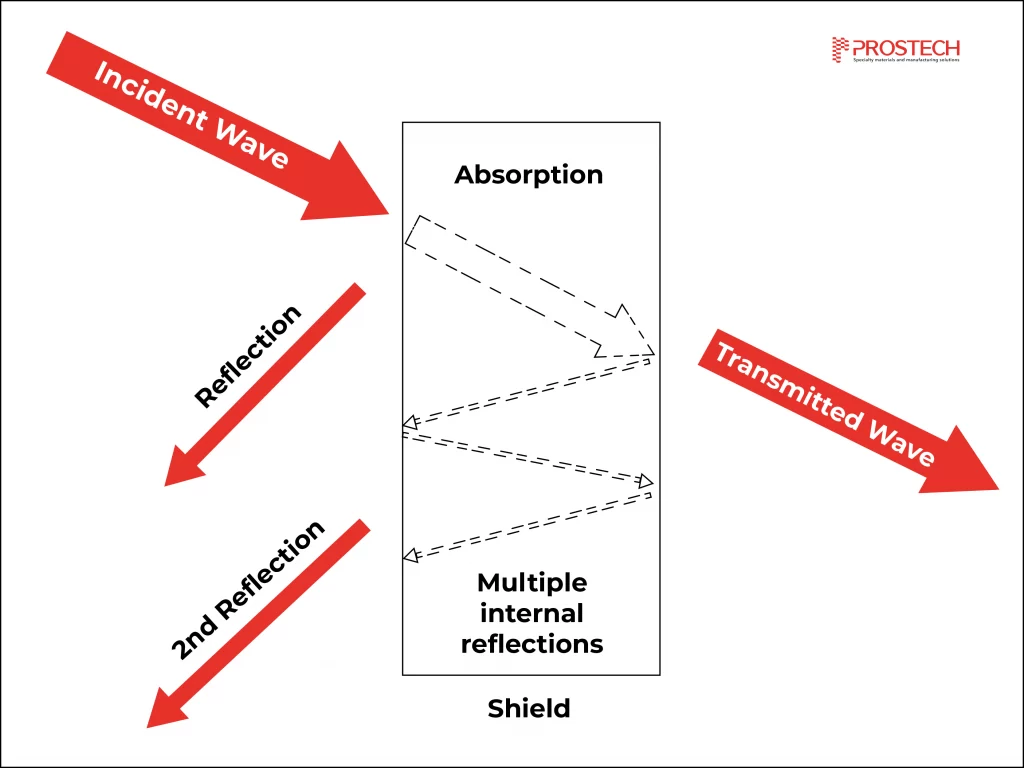

- Reflection: This mechanism reduces the electromagnetic wave component through reflection. The higher the conductivity of the material, the better the anti-electromagnetic interference effect. However, the existence of discontinuities or gaps larger than the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave can reduce the anti-interference effect. Therefore, reducing the size of the openings in the shielding shell is very important.
- Absorption: This mechanism requires materials that are electrically and magnetically conductive. They have the ability to absorb electric and magnetic fields by creating a conduction path within themselves. However, these materials usually have low electrical conductivity.
- Multiple Reflection: This mechanism often occurs in composite materials with large surface areas or porous structures. They allow multiple reflections of electromagnetic waves, resulting in scattering.
Effective materials for EMI Shielding
From the mechanism of electromagnetic interference, it can be seen that the main properties required for electromagnetic interference materials are electrical conductivity and magnetism. Commonly used materials for electromagnetic interference include metals, carbon isotopes, intrinsically conductive polymers, silicones, foams, silver plating and anti-interference fabrics.
EMI Absorber
Electromagnetic Absorbers protect PCBs and electronic devices by absorbing electromagnetic waves. They are commonly supplied in sheet, tape and foam form, which can be cut into 2D shapes as required.


- Silicone Materials absorb EMI: Gluditec EMI6425, BERGQUIST GAP PAD TGP EMI4000, LOCTITE SI 5421, Momentive SnapSil CXE16-0226B
- Flexible, Elastic Materials block noise and absorb EMI: 3M™ EMI Absorber AB6000, AB6000S, and AB6000G Series, VieTape EMI70 Series
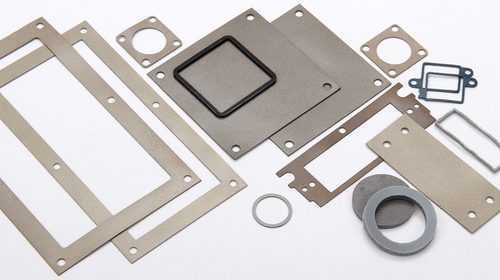
EMI Gaskets
EMI Gaskets are used to seal gaps in shielding enclosures and prevent electromagnetic waves from leaking into or out of the device. EMI Gaskets are resilient, easy to install, and can be customized to fit a variety of devices and applications. In addition to o-rings, foams, conductive adhesives are also a popular choice, especially for complex surfaces, where machining gaskets into many shapes will cost more than using conductive adhesives.

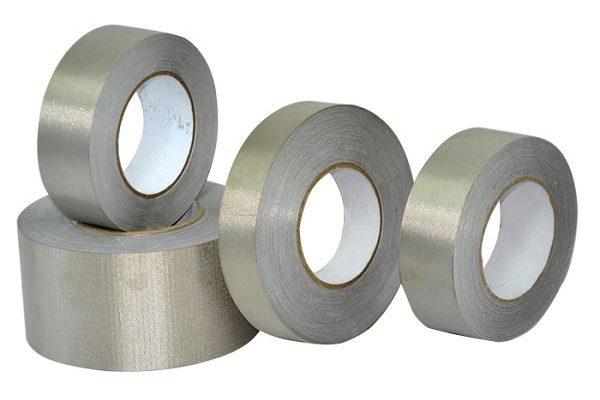
EMI Shielding Tape – Cable Shielding
EMI Shielding Tape is usually made from conductive materials such as aluminum, copper, or conductive fabric. EMI Shielding Tape is wrapped around the cable to create a protective shield, preventing the intrusion of electromagnetic waves from the outside and minimizing the emission of electromagnetic waves from inside the cable.


- Conductive and Thermally Conductive Adhesive Tapes: 3M™ Electrically Conductive Double-Sided Tape 9711S Series
- Aluminum and Fabric Tapes: Băng keo nhôm 3M™ EMI 1170
- Conductive and Thermally Conductive Foam Tapes: tesa® 60246, Tglobal – TGJ3C Electrically Conductive Cushion Tape
Solid enclosures
Solid enclosures are typically made of metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, or aluminum-copper alloys. These metal enclosures act both as structural support or a frame for the device or circuit board, and as a barrier to electromagnetic waves from entering or leaving the system. The enclosure is grounded so that if there is a leakage current, it will be conducted to the ground, reducing the risk of electric shock.
EMI coatings
These types of coatings are commonly applied to the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs), microchips and other electronic devices to minimize the effects of electromagnetic interference and ensure stable operation of electronic components. The main features of EMI coatings include:
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Shielding: Prevents the intrusion of external electromagnetic interference into electronic equipment.
- Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) Shielding: Prevents the intrusion of magnetic interference from external magnetic interference sources.
- Anti-Oxidation: Protects component surfaces from oxidation and other environmental impacts.
EMI coatings are generally divided into two main categories: conductive coatings and thermally conductive coatings. Conductive coatings are typically made from conductive materials such as graphite, carbon, or conductive metals to create a coating that is electrically conductive and noise-resistant. Meanwhile, thermally conductive coatings are typically made from conductive polymers or metal compounds to create a coating that is both anti-magnetic and heat-resistant.
Prostech is a specialist in providing EMI protection solutions, you can search for suitable products from the electromagnetic interference shielding product catalog here:
With years of experience in the industry and a deep understanding of EMI protection solutions, we are committed to providing you with the highest quality and most suitable solutions. Contact us today for a free consultation to choose the most suitable EMI shielding materials for each application.