In the process of manufacturing and assembling electronic devices, thermal management is always one of the issues that manufacturers are particularly concerned about. High temperatures can cause overheating, reducing the life and performance of the device. Although thermal paste/thermal grease is a popular solution, it still has many limitations such as difficulty in application, watse,… To solve the above problems, thermal pads have become a more suitable choice for many applications. So what is a thermal pad, what types are there, and what are the outstanding advantages of thermal pads compared to thermal grease? Find out in this article!
See all the thermal management solution
Definition of Thermal Pad
Thermal Pad (thermally conductive or thermal interface pad) are a preformed square or rectangle of solid material (often silicone-based). These are commonly used underside of the heatsink to aid the conduction of heat away from the component being cooled (such as CPU or another chip) and into the heatsink.
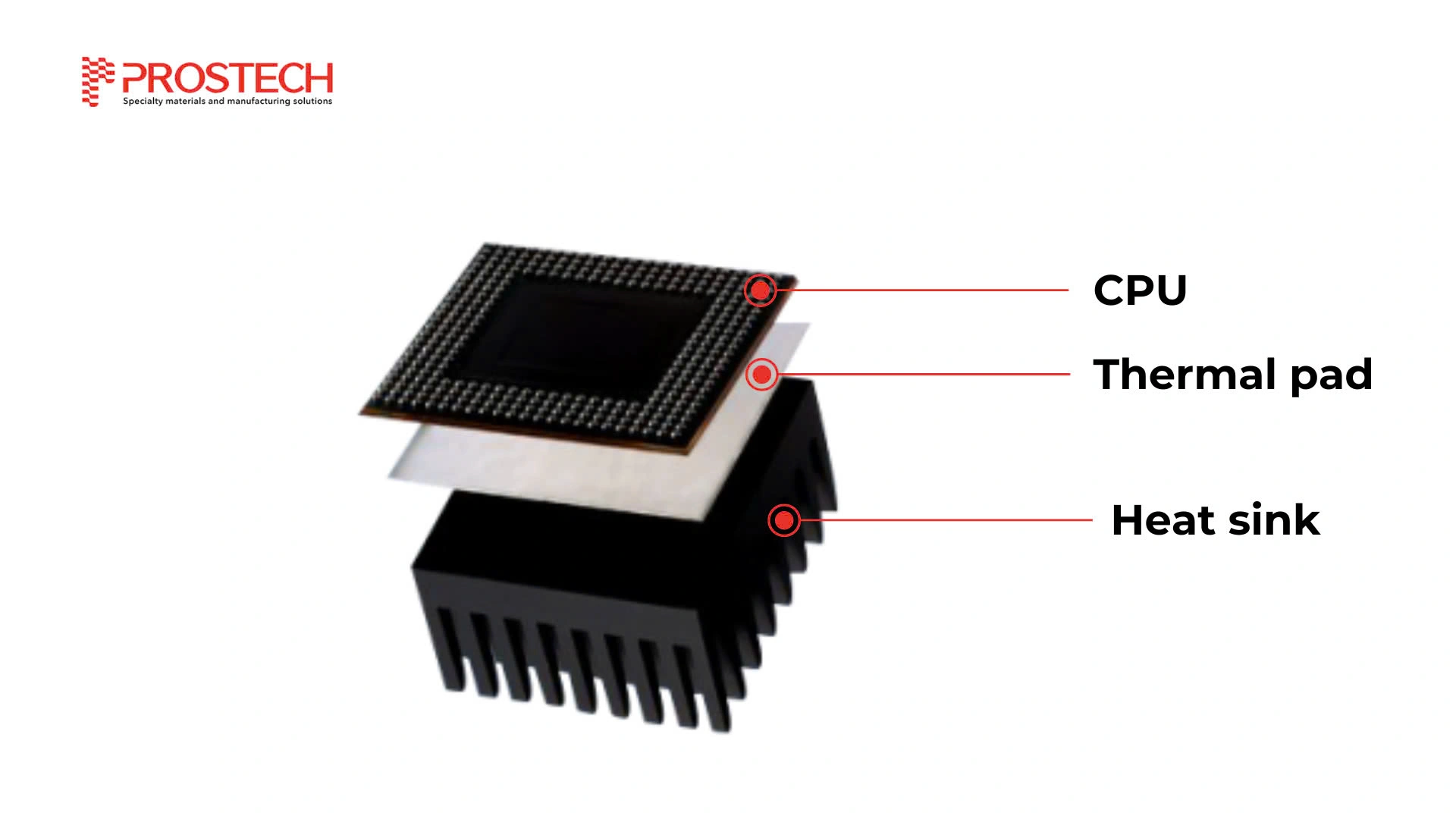

Air gaps between two non-flat surfaces hinder heat transfer due to air’s low thermal conductivity. Eliminating these air gaps enhances heat dissipation. Thermal pads fill these air gaps between non-flat surfaces, eliminating air pockets and consequently improving heat transfer efficiency.
Types of Thermal Pad
According to the material bases
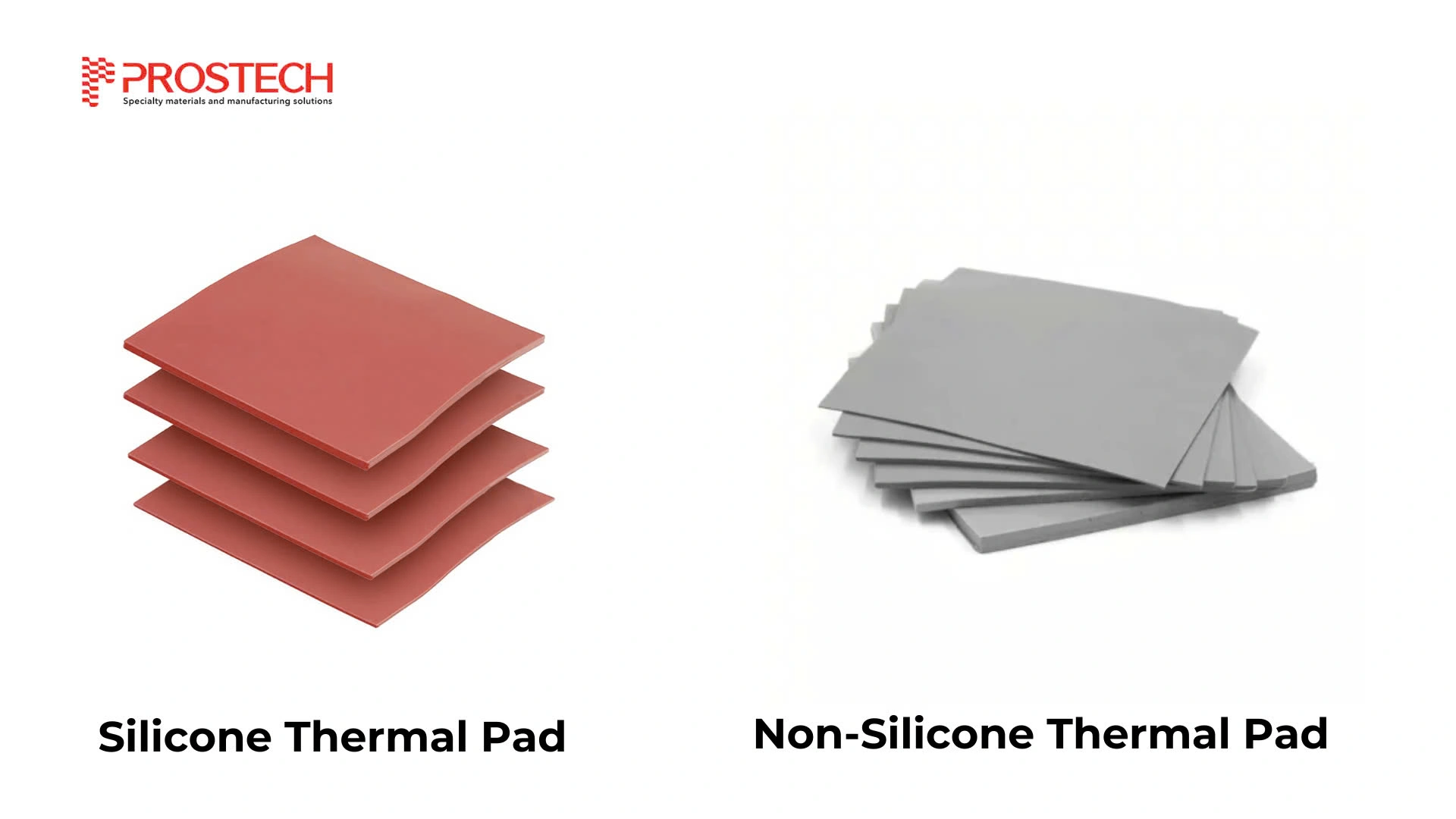

- Silicone based: Silicone is the most widely used chemical in thermal interface materials (TIMs) due to its superior thermal conductivity, surpassing that of conventional polymer materials. Additionally, silicone exhibits excellent compressibility and high-temperature resistance, ensuring long-lasting heat dissipation performance.
- Non-silicone based: Avoid depositing silicone oil at room temperature, usually used in high-end medical equipment such as precision optics and LEDs. No volatiles to the optical window and will not contaminate the PCB. Otherwise, it is also used in many applications such as: IC, CPU, MOS, LED, M/B, P/S, Heat Sink, LCD-TV, Notebook PC, PC, Telecom Device, Wireless Hub, DDR II Module, DVD Applications, Hand-set applications, etc.
According to the structure
- Thermal Pad with Adhesive: This type of thermal pad is designed with a layer of adhesive pre-applied on one or both sides of it. This adhesive layer has a sticky feature, which helps the thermal pad adhere firmly to the surface of components or heatsinks without the use of other adhesive media.
- Thermal Pad without Adhesive: This thermal pad does not have a built-in adhesive layer. Instead, it relies on weight or pressure from other components in the system to stay in place.
Advantages of thermal pads over thermal paste


The biggest advantage of thermal pads is their ease of use and replacement. They are pre-formed and cut to the right size for the application, making them very flexible. As a result, users do not need to worry about using too much or too little material as they do with thermal paste. This helps avoid wasting material costs or not achieving the desired performance. Thermal pads also help shorten the process, such as cleaning the surface of the heat sinks whenever they need to be replaced.
In addition, the thermal pad is also a type of phase change material that has been preformed thanks to its ability to change its physical properties depending on suitable conditions. These pieces will be solid, stable at room temperature, cut into sizes that fit the surface of electronic components, easy to use. However, the thermal pad will gradually soften when the temperature increases. This is a mechanism to adapt to changes in the surface of components and thermal pad when there are air-filled holes that hinder the heat dissipation process.
In many cases, the thermal conductivity of the heat sink will not be as good as that of the thermal paste. Depending on the application, the user needs to choose the most suitable thermal interface material.
In addition to thermal pad, there are a number of other thermal interface materials such as:
Read more about thermal interface materials at: Common Types of Thermal Interface Materials TIMs
Applications of Thermal Interface
Thermal Pads have many important applications in fields such as:
- Computer and electronic components: Used in CPUs, GPUs, RAM, and motherboards to transfer heat from these components to thermal interface, helping to prevent overheating and maintain performance.
- Consumer electronics: Used in phones, tablets, and handheld game consoles to manage heat from the processor chip and battery.
- Telecommunications equipment: Used in routers, modems, and networking equipment to ensure stable operation.
- Industrial equipment and automotive: Used in industrial and automotive electronic systems to manage temperature and protect components.
- Power supplies: Used in computer power supplies, chargers, and power adapters to control temperature and prevent overheating.


Conclusion
Heat dissipating materials play an important role as an effective heat conduction “bridge” between electronic components, helping them operate stably. Thereby extending the life and improving the performance of the device. With the increasingly rapid development of the electronics industry, heat dissipating materials have become indispensable materials in electronic devices.
However, choosing the right thermal pad is not simple, depending on many factors such as size, thickness and material properties to meet the needs of each specific application. On the market today, there are many types of thermal pads available with sizes from thin to thick, commonly 2mm thermal pad, 1mm thermal pad,…
Prostech is the official distributor of thermal pads from big brands such as 3M, t-Global, Gluditec và Jones Tech,… With many years of experience, Prostech has provided products to thousands of large and small manufacturers nationwide. Not only providing products, Prostech always strives to create the best values for customers through support and professional advice to meet the specific needs of customers. Contact us for free consultation!