With the global push toward lower carbon emissions, automakers are rapidly transitioning from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs). While EVs offer clear environmental benefits, they present new challenges—chief among them is managing the added weight of batteries. To ensure optimal performance and extended battery range, reducing the overall weight of EVs has become a top priority. This article explores how low-density materials are revolutionizing EV design and driving the future of sustainable mobility.
Solution for automotive industry
Methods to reduce weight in EV design
1. Replacing heavy materials with lightweight material
One of the most effective strategies is replacing heavy materials, such as traditional steel, with lightweight alternatives. Materials like aluminum, magnesium alloys, and polymer composites are increasingly used in vehicle structures, offering a balance between weight reduction and durability.
In some cases, manufacturers combine different lightweight materials to achieve optimal performance. For example, polycarbonate—a lightweight, impact-resistant plastic—is often paired with aluminum to create components that are both strong and lightweight. This hybrid approach allows engineers to maintain structural integrity while significantly reducing mass, which is particularly beneficial for electric vehicles (EVs) that require weight reductions to maximize battery efficiency and driving range.

2. Adhesive bonding of lightweight materials
As the industry shifts toward lighter materials, traditional mechanical fastening methods—such as bolts, screws, and welding—become less effective. These fastening techniques not only add weight but can also create stress concentration points, leading to potential structural weaknesses.
To address these challenges, adhesive bonding has emerged as a superior solution for joining lightweight materials. Unlike mechanical fasteners, adhesives evenly distribute stress across bonded surfaces, reducing the risk of material fatigue and improving durability. Additionally, adhesive bonding enables seamless connections between dissimilar materials (e.g., aluminum and polymer composites), which would otherwise be difficult to join using conventional methods.
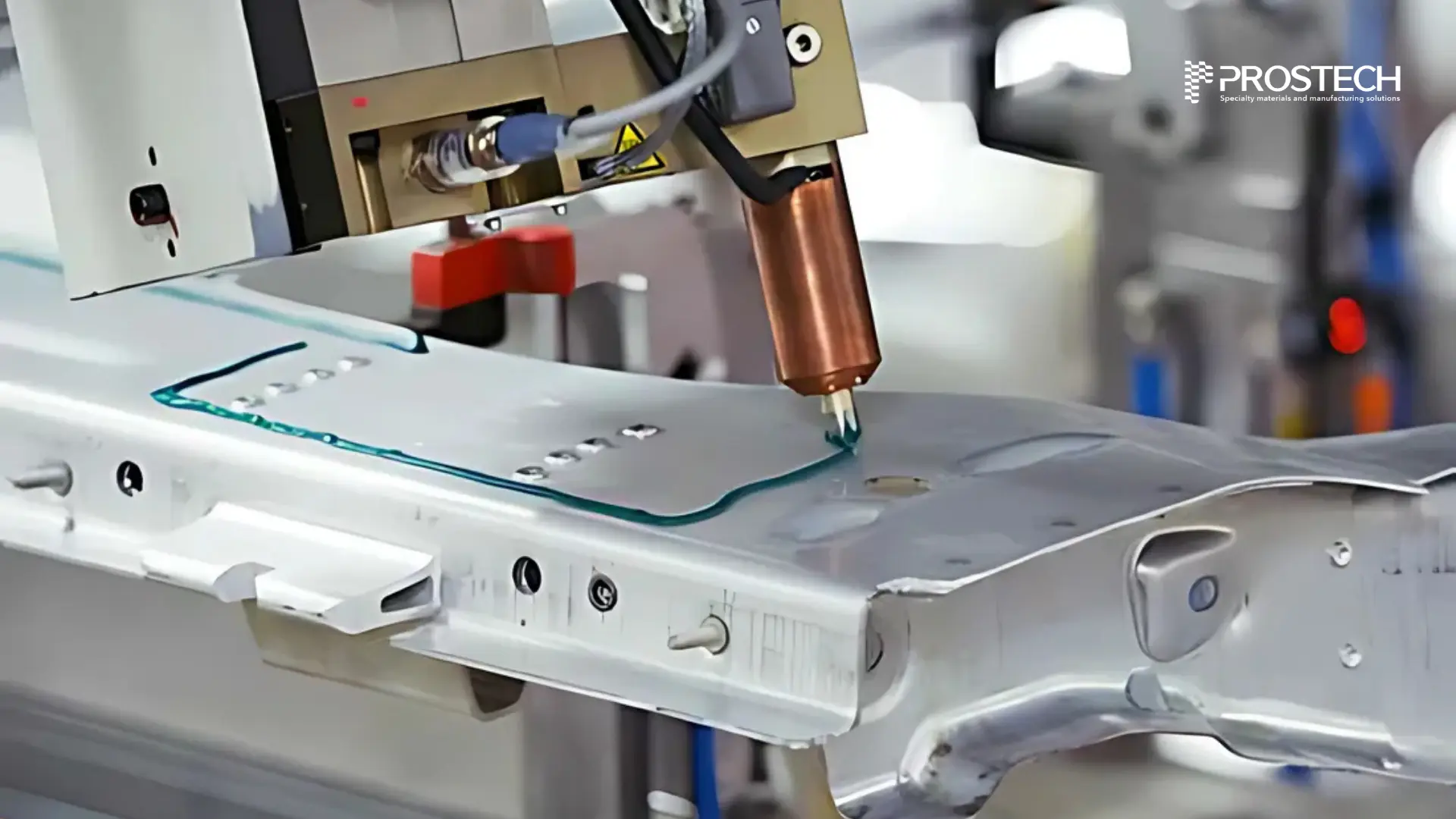


Industry projections indicate that by 2030, approximately 67% of materials used in vehicle manufacturing will be lightweight materials. As this trend accelerates, adhesives will play an increasingly crucial role in ensuring the integrity, efficiency, and longevity of next-generation vehicles. Whether you’re looking to enhance structural integrity, improve thermal management, or reduce overall weight, our team of experts is here to help. Contact us today for a consultation!
Low-density materials in adhesive bonding technologies
In lightweight electric vehicles (EVs), various adhesive bonding technologies are used to enhance structural integrity, thermal management, and overall efficiency. Here are some key adhesive technologies commonly applied in EV manufacturing:
1. Structural adhesives & sealants
These adhesives are used to bond lightweight materials, replacing traditional welding and mechanical fasteners. They help distribute stress evenly across the bonded surfaces, reducing material fatigue and improving crash resistance.
Applications:
- Body panels
- Battery enclosures
- Composite structural components
Benefits:
- Weight reduction
- Improved durability
- Enhanced corrosion resistance
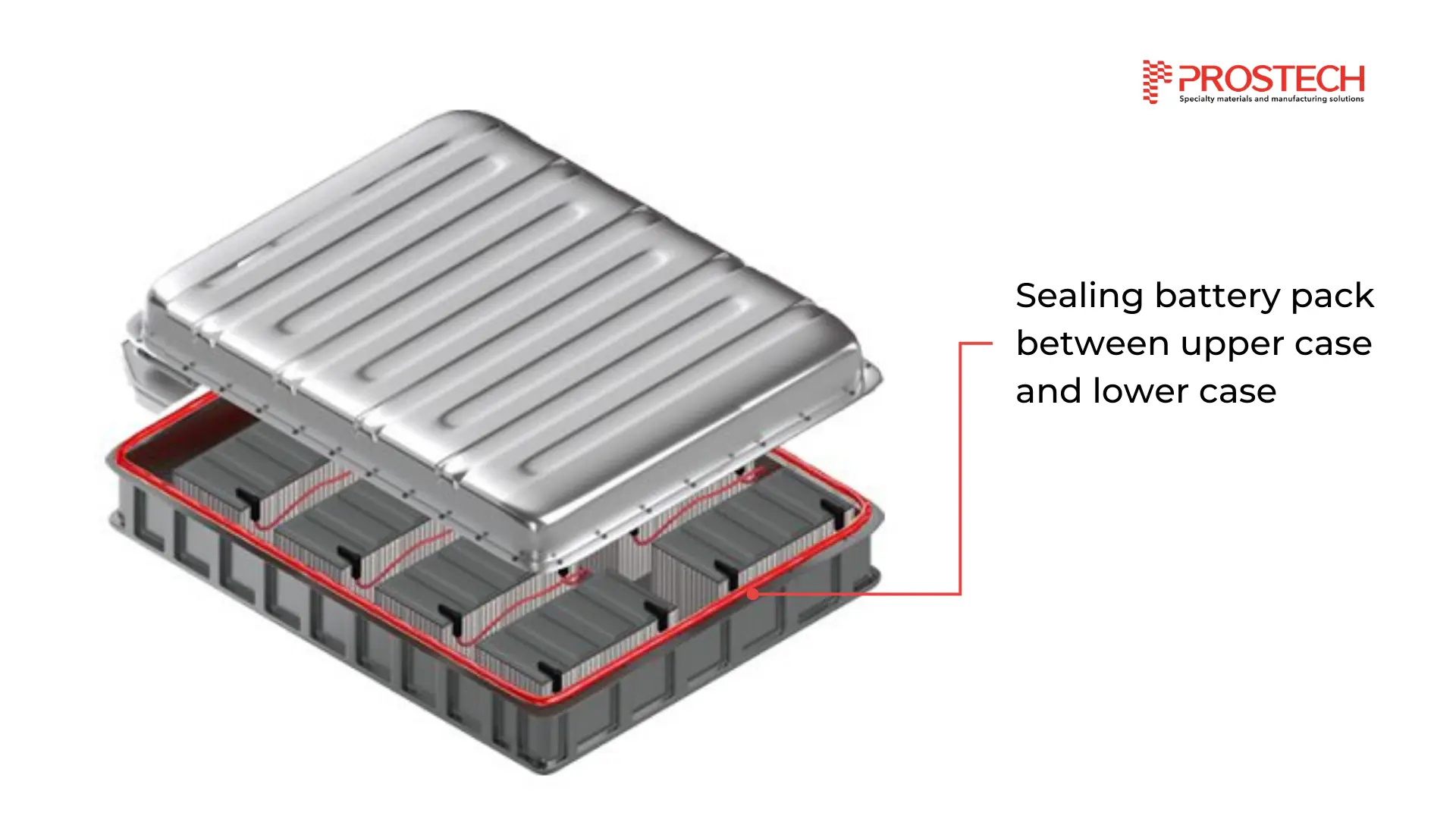

Structural Bonding Adhesive Solutions
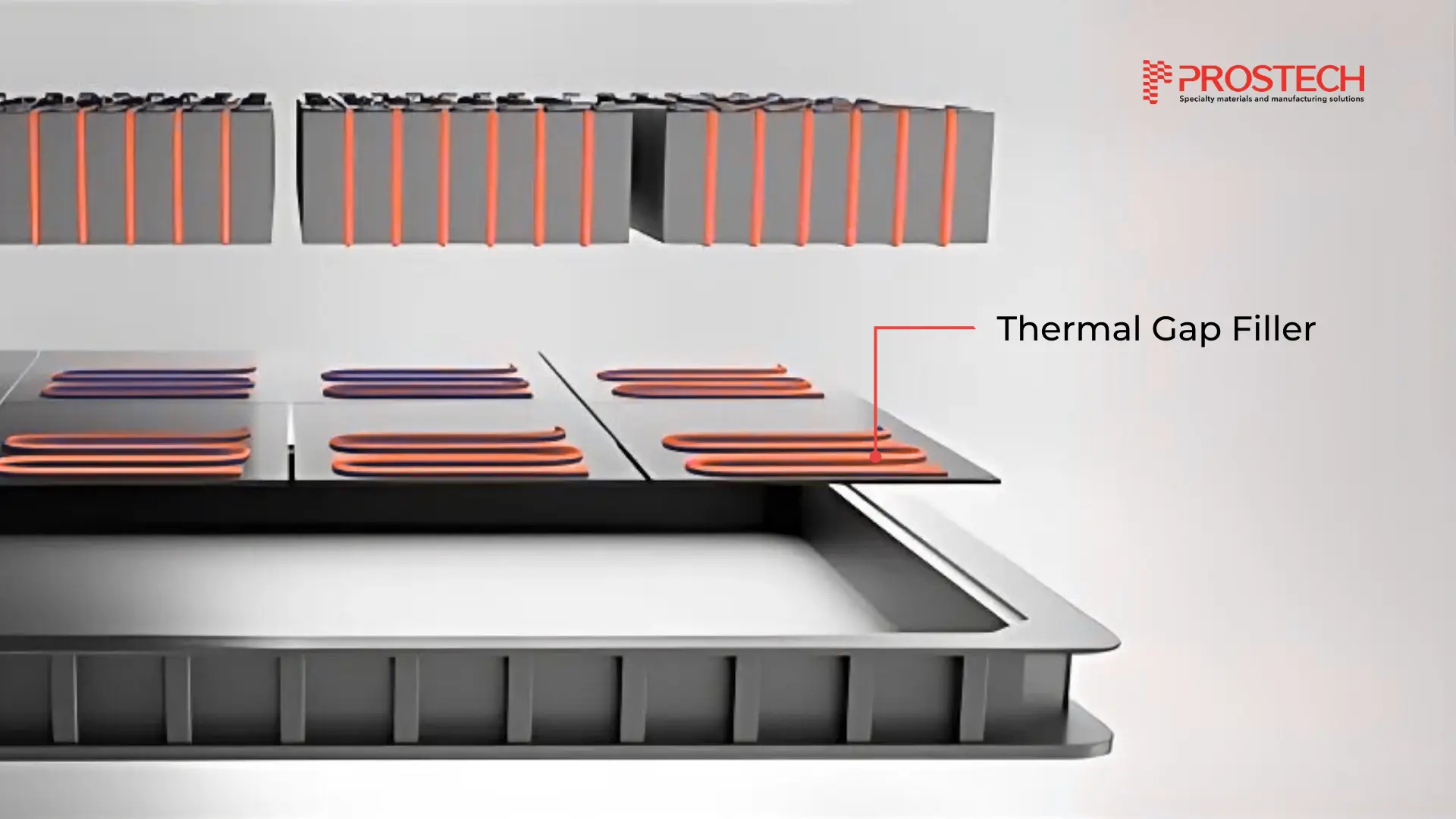
2. Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs) – Low-density Gap Fillers
TIMs are essential for battery pack assembly, where they help efficiently transfer heat away from critical components to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability. Low-density TIM gap fillers, such as silicone-based thermal pastes or phase change materials, help reduce weight while maintaining excellent thermal conductivity.
Related article: Common Types of Thermal Interface Materials TIMs
Applications:
- Between battery cells
- Power electronics
- Heat sinks
Benefits:
- Thermal management
- Weight optimization
- Increased battery efficiency

3. Thermal adhesives
These adhesives serve a dual purpose: mechanical bonding and thermal conductivity. They are used in applications where components require both strong adhesion and heat dissipation.
Applications:
- Battery module assembly
- Powertrain bonding
- Electric motor components
Benefits:
- Improved heat dissipation
- Lightweight bonding solutions
- Increased component lifespan


The choice of the appropriate low-density materials depends on the specific requirements of the application. Each type of material offers its own advantages and is suited to different demands during the manufacturing and usage processes. With many years of experience in the industrial material, Prostech is ready to assist customers in selecting the right low-density materials and providing integrated solutions for production lines to optimize manufacturing efficiency. Contact us for free consultation.