Low Pressure Molding (LPM) is a method that uses a layer of material to mold and encase electronic components, protecting them from external environmental impacts. Today, LPM is becoming increasingly popular due to its notable advantages such as excellent protection, low pressure, and particularly its fast molding process and waste reduction. One of the key factors influencing the final product quality is selecting the appropriate low pressure molding materials. Manufacturers today face the challenge of not only ensuring product quality but also balancing cost, durability, and heat resistance of the material. There are two main types of materials commonly used in LPM: thermoplastic and thermosetting, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. In this article, we will provide information about low pressure molding materials, their properties, and how to choose the right material for each application.
Learn more about this method at: Overview of Low Pressure Molding: Benefits and Applications
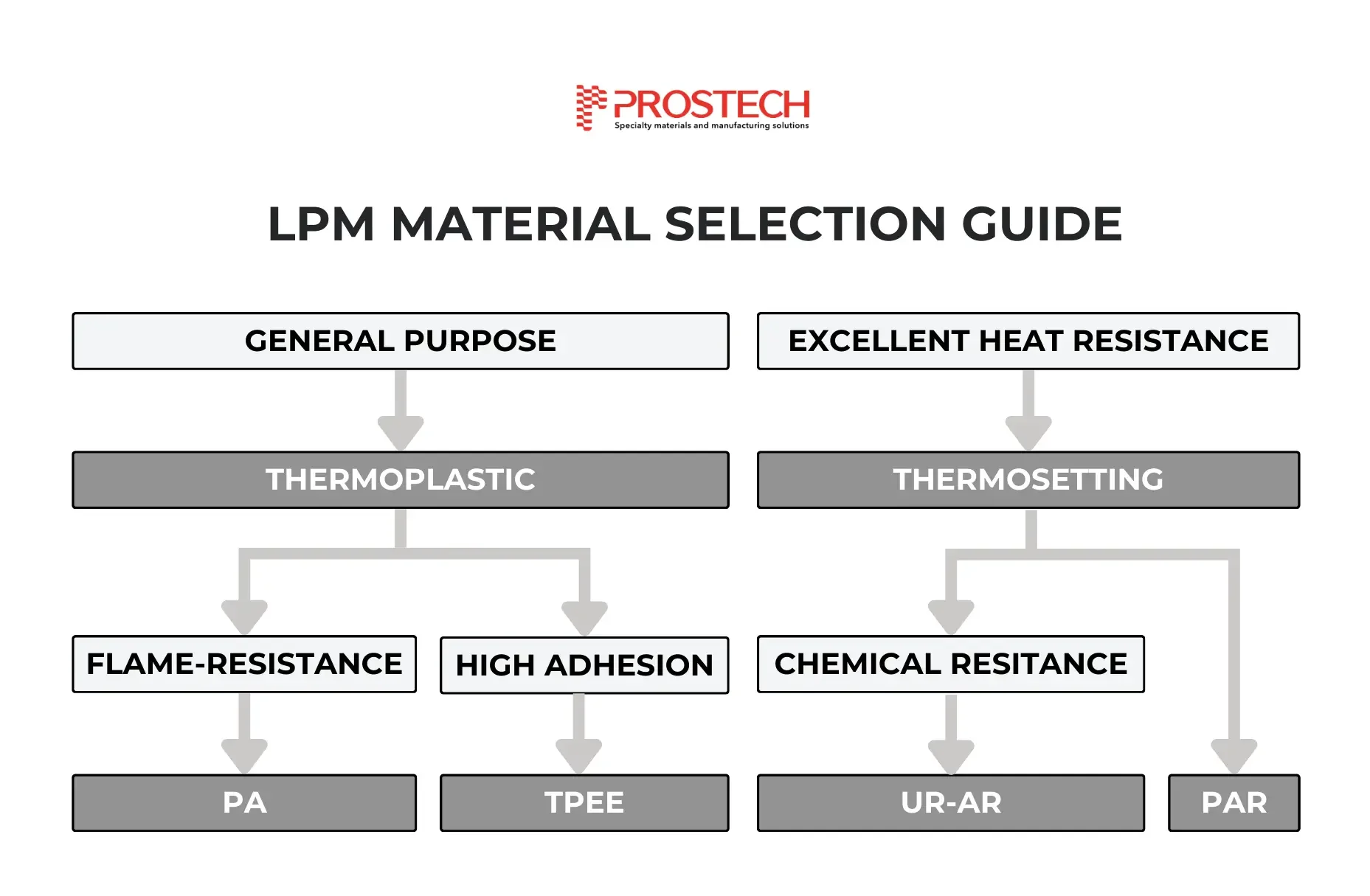
I. Low pressure molding materials: Thermoplastic
Thermoplastics are types of material that can be processed at high temperatures and will harden upon cooling. These materials offer good thermal, mechanical, and chemical resistance, and they are recyclable and easy to process. In low pressure molding, thermoplastics such as Polyamide (PA) and TPEE are commonly used.
1. Polyamide (PA) – Common low pressure molding material
Polyamide (PA), also known as Nylon, is distinguished by its superior mechanical strength, high durability, and abrasion resistance. This material has good thermal stability and chemical resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. PA has an amide structure -CONH- with polymer chains linked by hydrogen bonds. As a result, PA has excellent impact and vibration absorption properties and is easy to process due to its relatively wide glass transition temperature (Tg) and melting point (Tm).
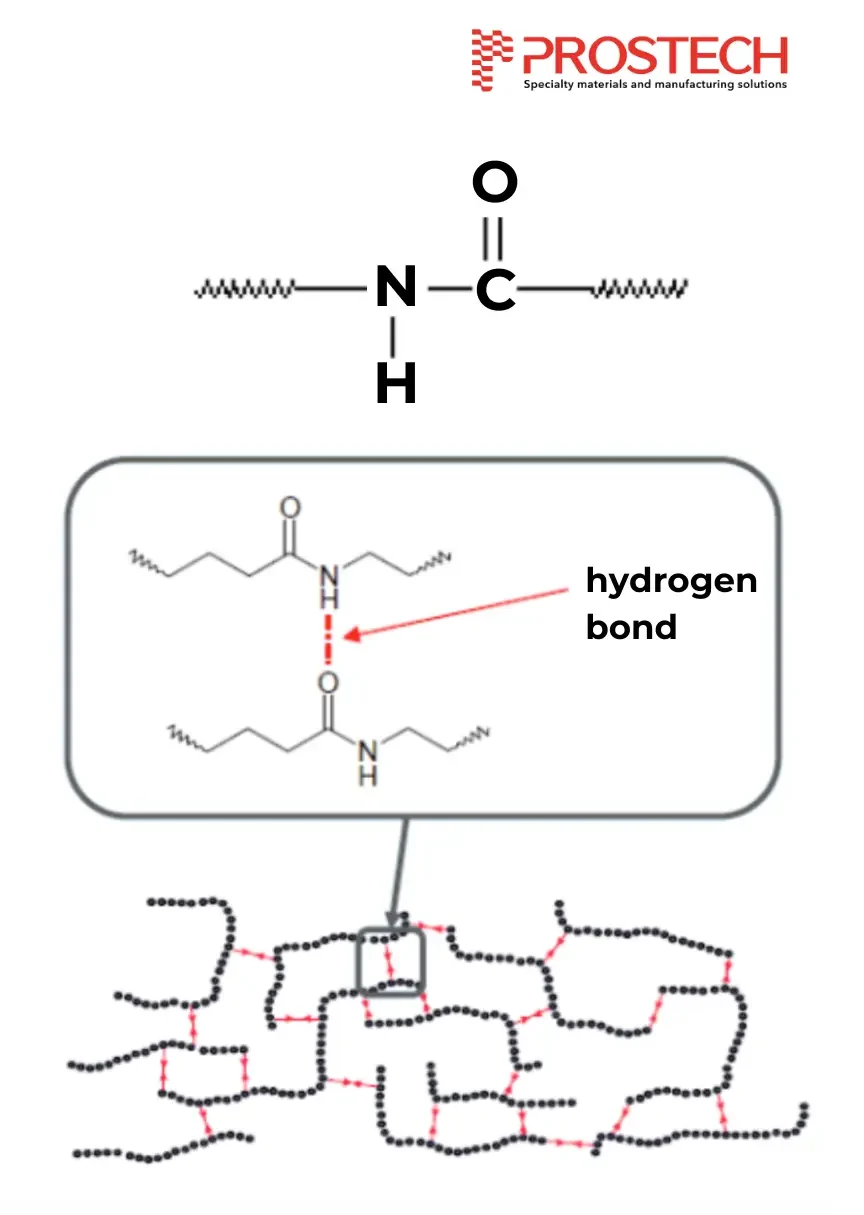
Advantages of Polyamide (PA) Material in Low Pressure Molding:
-
PA has excellent impact and vibration resistance, making it suitable for applications that require high durability.
-
PA is easy to process due to its low viscosity.
-
It can withstand temperatures ranging from 125°C to 150°C, depending on the type of PA.
-
PA maintains its impact resistance at low temperatures due to its special polymer structure.
-
PA is resistant to non-polar solvents.
Disadvantages of Polyamide (PA) Material in Low Pressure Molding:
- PA tends to absorb moisture, requiring drying before processing or the use of improved PA to reduce water absorption.
- PA is not resistant to polar solvents.
- PA has poorer adhesion compared to TPEE in some cases.
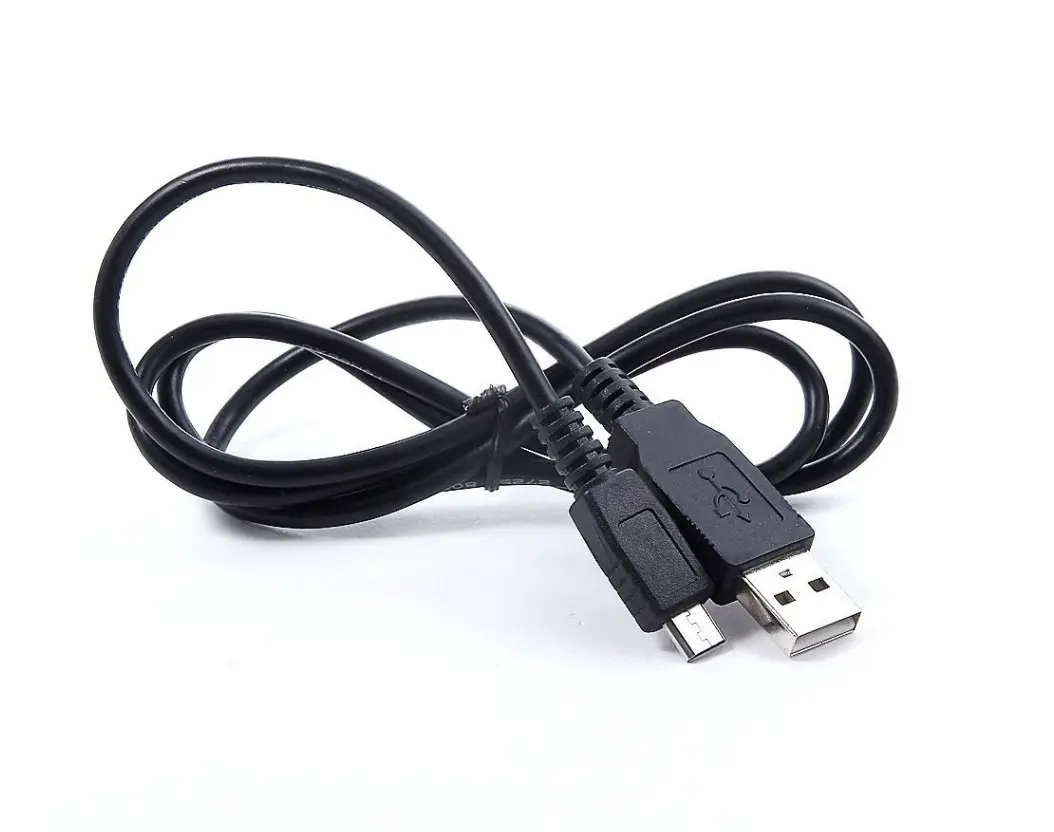
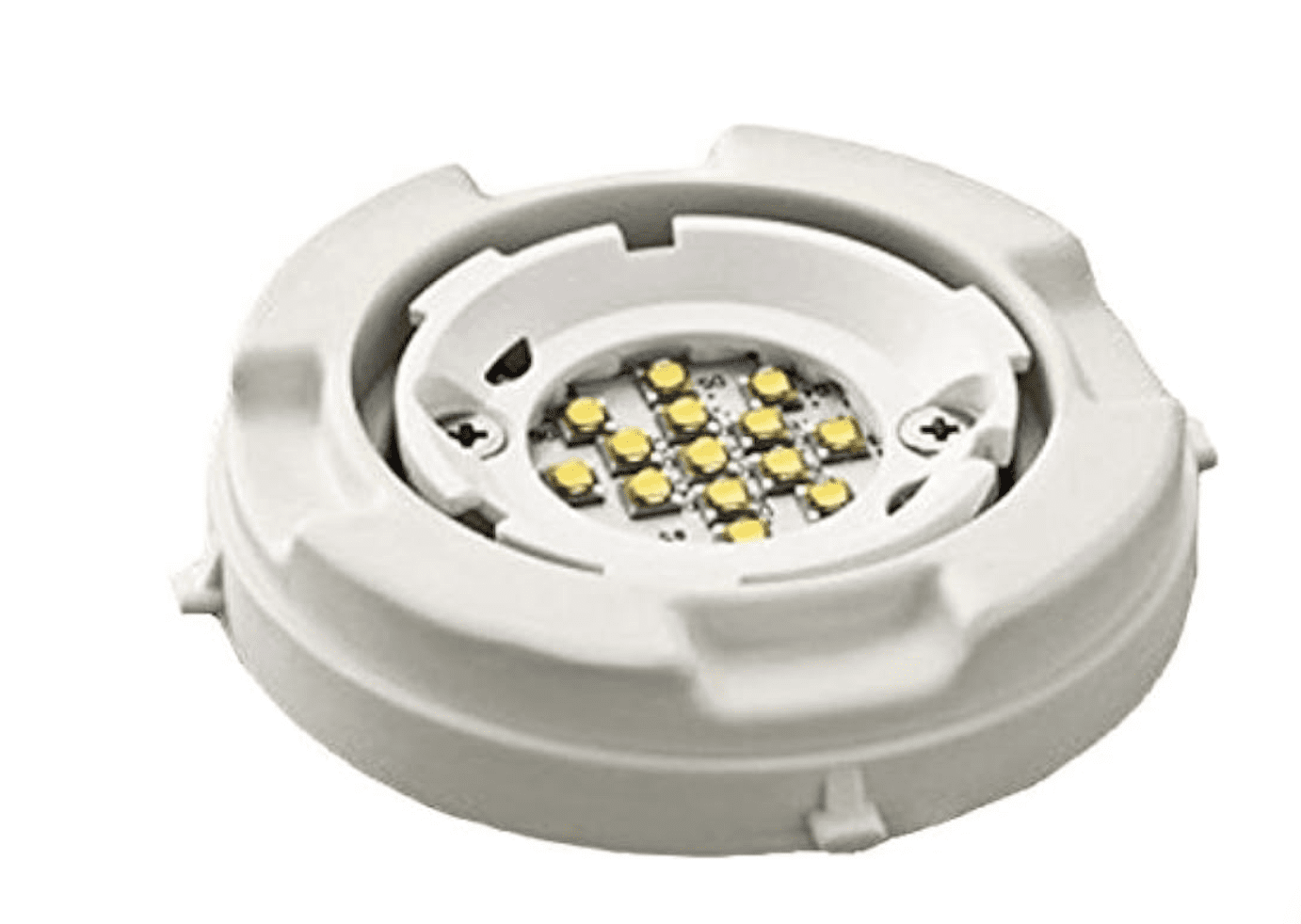
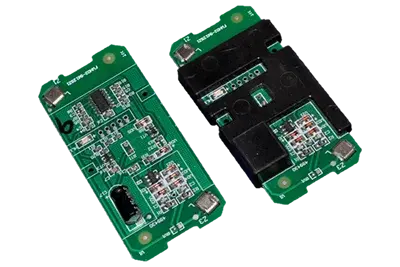
Applications of Polyamide (PA) in Low Pressure Molding: PA is used in various applications including control devices, sensors, PCBs, cables, connectors, batteries, antennas, LEDs, and more.
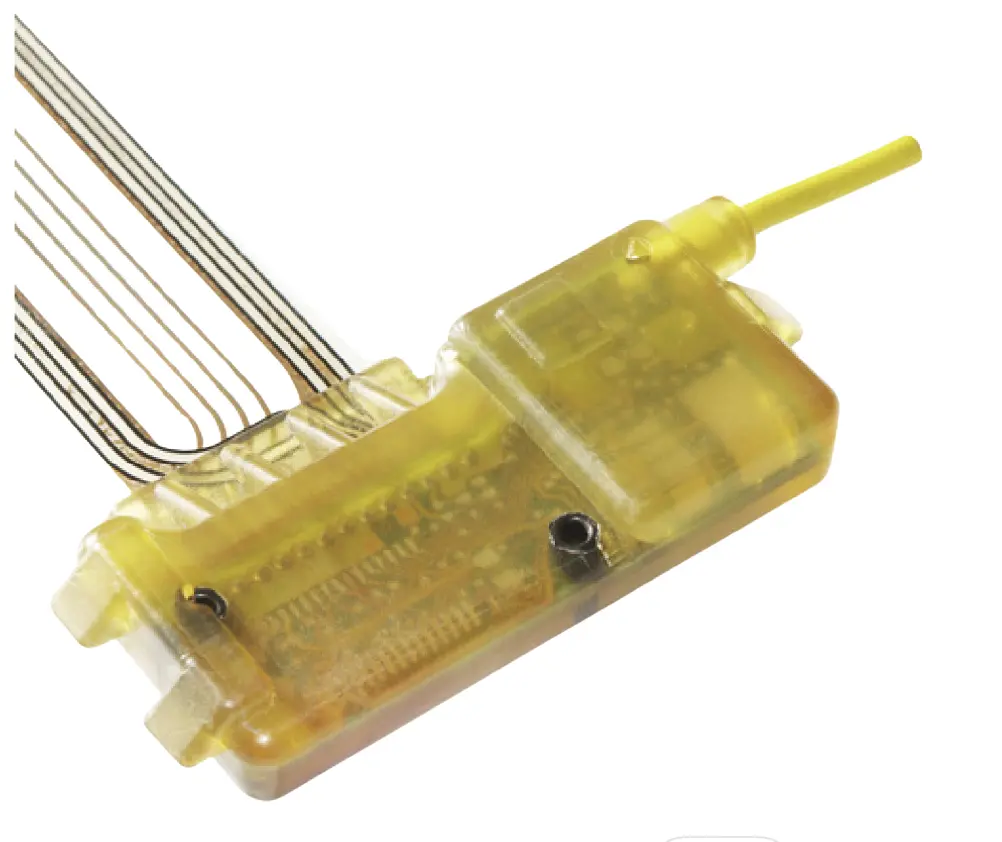 |
 |

|
| Printed Circuit Board | Cables | LED |
2. TPEE (Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer)
TPEE has an ester linkage structure combined with elastomer, providing flexibility and good adhesion to a variety of surfaces.
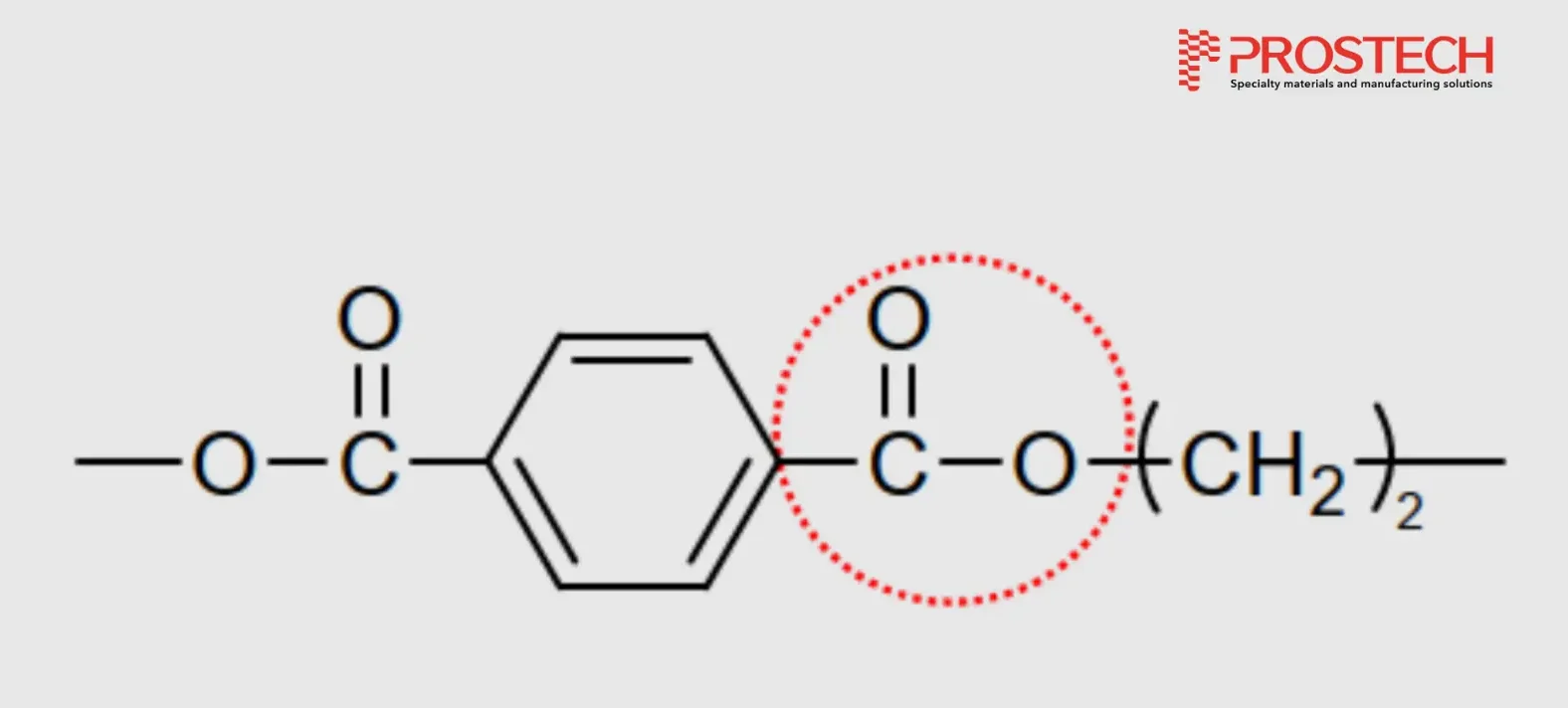
Advantages of TPEE Material in Low Pressure Molding:
- TPEE adheres well to various surfaces such as FPC, PBT, FR-4, PI, etc.
- It performs well under prolonged exposure to heat and moisture.
- TPEE can withstand extremely low temperatures down to -40°C, with a Tg range of -75°C to -40°C.
- The combination with elastomer gives TPEE high flexibility.
- TPEE is resistant to polar solvents like alcohol.
Disadvantages of TPEE Material in Low Pressure Molding:
- TPEE has limited flame resistance and may require special formulations to improve fire resistance.
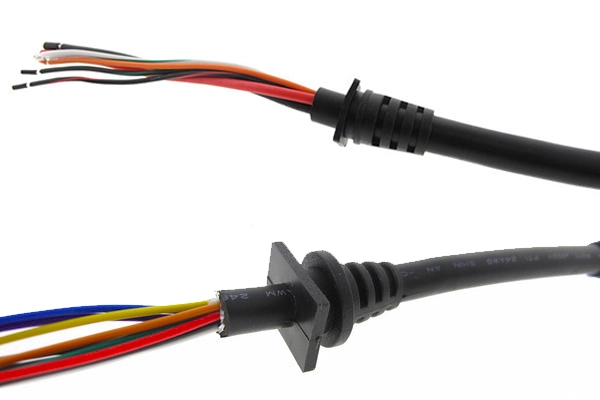
Applications of TPEE in Low Pressure Molding: TPEE is commonly used in applications such as ECU, sensors, coils, LEDs, modules, PCBs, heat shrink tubing, FPC,…
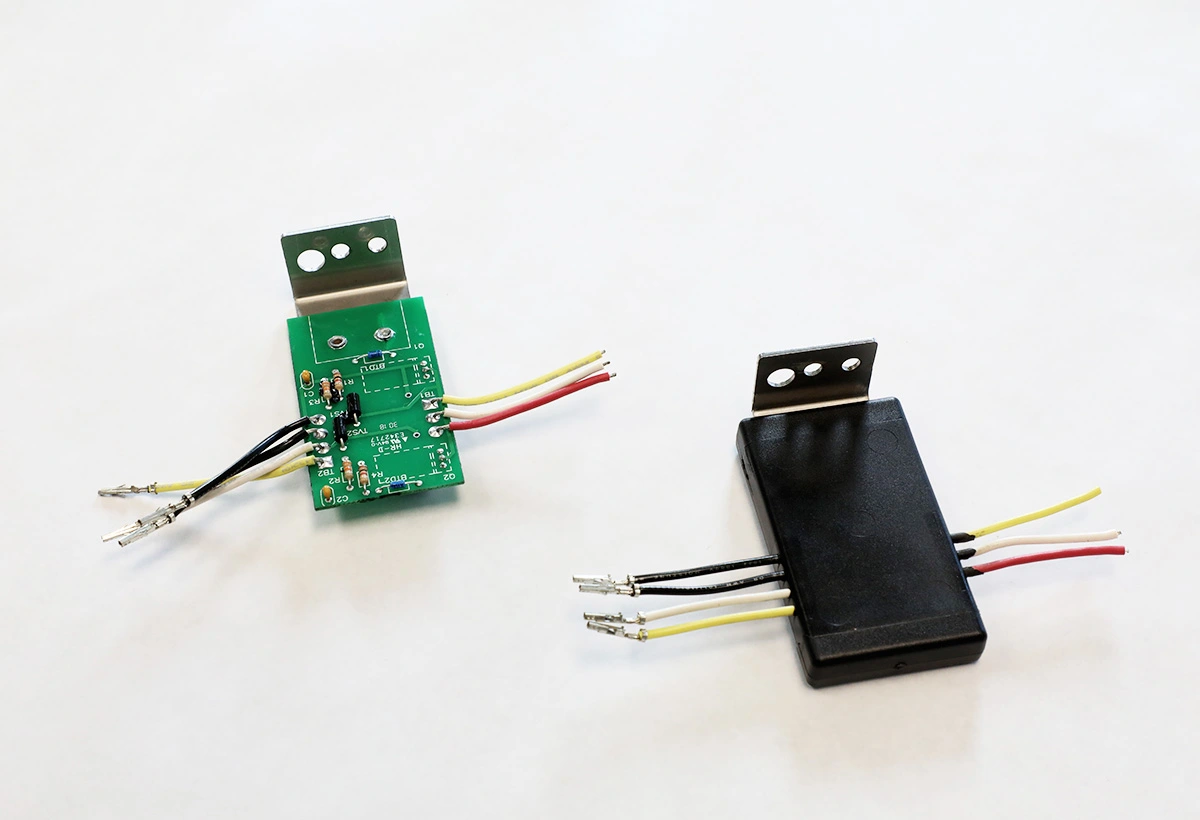 |
 |
 |
| Sealing of flexible substrates | Sealing harnesses and wiring parts | Partial encapsulation of substrate |
II. Low pressure molding materials: Thermosetting
Thermosetting plastics are types of plastics that, once cured and hardened, cannot be melted or recycled. These materials are often used for applications requiring high heat and chemical resistance.

1. Reactive Polyamide (PAR)
Reactive Polyamide (PAR) has a three-dimensional network structure with cross-links, providing exceptional heat resistance and durability.
Advantages of Reactive Polyamide (PAR) Material in Low Pressure Molding:
- PAR can withstand high temperatures due to its tightly bonded network structure, ranging from -55°C to over 200°C
- It is suitable for applications in harsh conditions due to its high strength
Disadvantages of Reactive Polyamide (PAR) Material in Low Pressure Molding:
- Non-Recyclable
Applications of Reactive Polyamide (PAR) in Low Pressure Molding:
PAR is used for molding electronic/electrical components, connectors, and cables that require extreme heat resistance,…
2. Urethane-Acrylate
Polyurethane-acrylate combines the advantages of both polyurethane and acrylic plastics. This material is notable for its excellent impact resistance, chemical resistance, and heat resistance. It has a low melting temperature but requires a high mold temperature to cure.
Advantages of Polyurethane-acrylate Material in Low Pressure Molding:
- Can withstand high temperatures for extended periods, up to 175°C for 3000 hours or 200°C for 1000 hours.
- Resistant to a wide range of chemicals.
- Provides high strength and durability.
Disadvantages of Polyurethane-acrylate Material in Low Pressure Molding:
- Cannot be recycled
Applications of Polyurethane-acrylate in Low Pressure Molding: Polyurethane-acrylate is commonly used for machine and engine components.
Beside materials, to learn more about options for molding systems, you can refer to the article: Overview of Low Pressure Molding Systems (Low Pressure Machine)
Guide to Choosing Materials for Low Pressure Molding (LPM)
So how should you choose the right material for the Low Pressure Molding (LPM) process?
Each application has specific requirements related to environmental conditions, durability, and resistance to external impacts. Understanding the criteria to consider when selecting a material will help you optimize the production process and enhance protection quality. To make an informed decision, manufacturers should consider three main factors:
- Environmental requirements: Evaluate factors such as temperature, humidity, exposure to chemicals, exposure to UV light, etc.
- Mechanical durability requirements: Assess attributes like hardness, flexibility, stress resistance, impact resistance, etc.
- Sealing requirements: Determine the necessary water resistance or airtightness level, such as IPX8 or a positive pressure of 50kPa.
Additionally, other criteria such as compatibility with the manufacturing process, aesthetics, and material costs should also be considered to ensure that the selected LPM material provides optimal performance for the application.
Prostech’s LPM Material Solutions
Prostech offers a range of LPM materials designed to fully meet the requirements for protecting electronic components from environmental and mechanical impacts. With a diverse selection of materials, from polyamide to polyolefin, Prostech provides solutions suitable for various applications, including high-temperature resistance, moisture resistance, chemical resistance, UV resistance, and more. These materials not only ensure excellent mechanical durability and perfect sealing but also offer good compatibility with manufacturing processes, optimizing costs for businesses.
 |

|
| Gluditec – HM3303 (Black & Amber): General purpose | Toyobo – VYLOSHOT® GM-960-R02: High adhesion |
Choosing the right low pressure molding (LPM) material depends on the specific requirements of the application and environmental conditions. Each type of material offers unique advantages and is suited to different needs during production and product use. We provide a comprehensive solution, including consultation, materials, and low pressure molding systems. With a international network of warehouses and logistics support, we are well-positioned as a comprehensive supplier. Prostech is committed to becoming a trusted partner for manufacturers around the world. Please contact us by leaving your information below:








